DDBJ and SRA Data Processing
The Bioinformation and DDBJ Center manages the DDBJ and Sequence Read Archive (SRA) databases of genetic sequence information. On this page and in the accompanying diagram you will find information about:
- how sequence data are submitted, processed, and made available to the public
- responsibilities of the sequence data submitter and the DDBJ Center
- transition of data status
Submitting Data
Sequence data submissions may be initiated by a variety of individuals including researchers, laboratory staff, sequencing center, data analysis center, and personnel associated with a data coordination center. Submitters deposit sequence data and metadata into DDBJ or SRA for many reasons including to:
- comply with data sharing policies established by government authorities, publishers, or funders
- support research community established principles such as the Bermuda Principles, or FAIR (findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable) data principles
- support open science
- serve the public good
Submitters are responsible for formatting their sequence data for submission, meeting submission standards, ensuring they have authority to submit the sequence data and using DDBJ services to submit the sequence data and metadata. At the time of submission, the submitter may specify a desired public release date for the sequence data (e.g., to align with the anticipated date of publication of a journal article). Submitters may request that private data be made publicly available prior to the scheduled release date or request that the release date be extended (e.g., to align with the anticipated date of publication of a journal article).
Processing Submissions
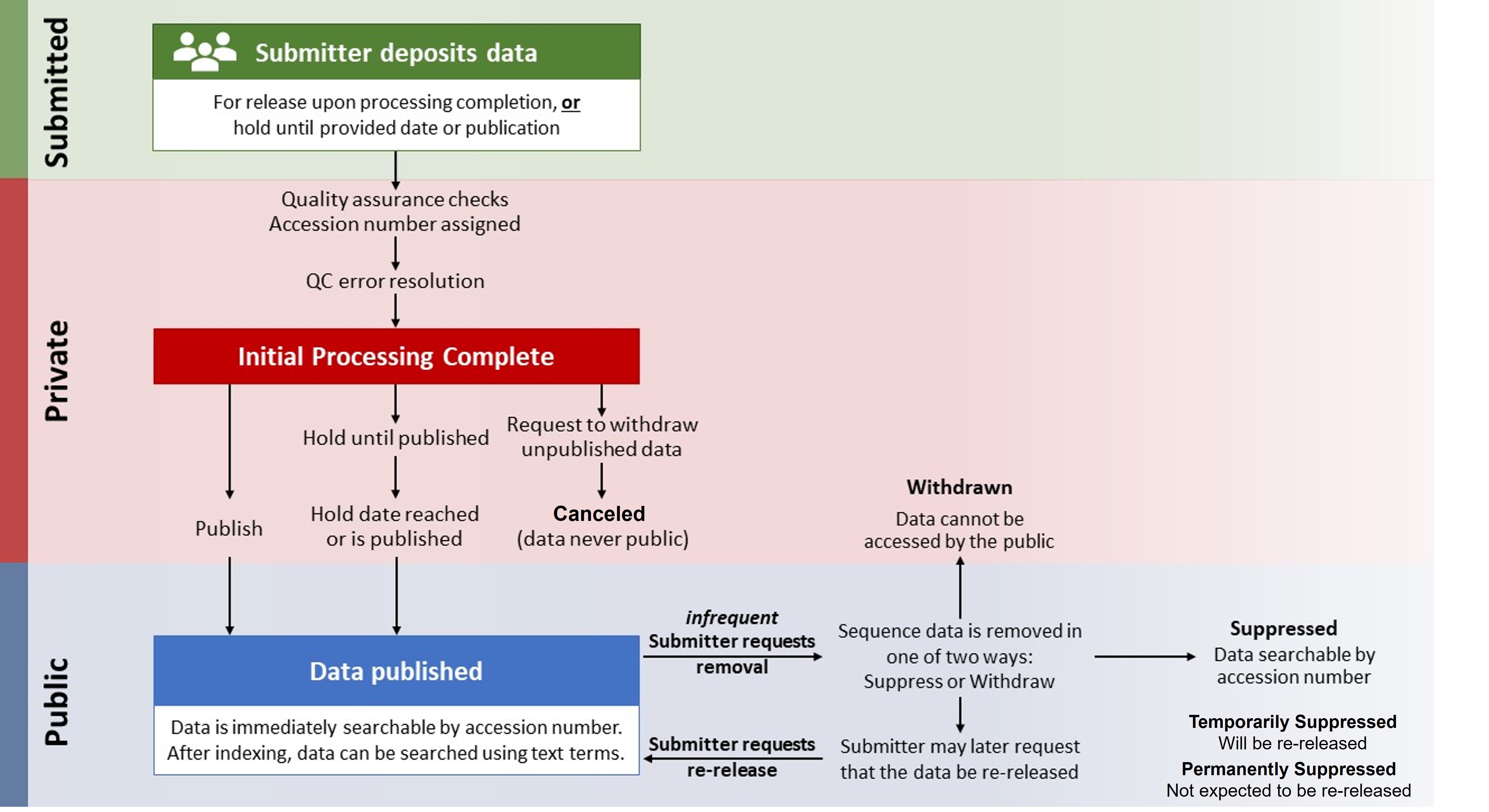
The DDBJ Center is responsible for processing submitted sequence data. Processing includes performing automated and manual checks to ensure data integrity, quality, and assigning accession numbers to submitted sequence data. The DDBJ Center holds the sequence data in a private status during processing, and prior to public release.
In general, the DDBJ Center processes submissions in the order received. However, the DDBJ Center may prioritize processing of submissions related to a pandemic or public health emergency. Upon the submitter’s request, the DDBJ Center may also prioritize processing of submissions associated with an upcoming publication release.
The DDBJ Center may halt the processing of submitted sequence data at any time prior to public release upon the request of the submitter. In this case, the DDBJ Center does not release the sequence data and retains the data in a canceled status.
The DDBJ Center may determine, based on quality control checks conducted as part of the processing, that the data are not of sufficient quality for public release. In such cases, the DDBJ Center will halt data processing and notify the submitter with an explanation. The DDBJ Center retains the sequence data in a canceled status.
Public Release and Data Accessibility
The DDBJ Center is responsible for making sequence data publicly accessible by putting them in a public status.
The DDBJ Center generally makes sequence data publicly accessible upon completion of processing or on the submitter-specified release date. According to the Data Release Policy, the DDBJ Center also makes sequence data that has completed processing publicly accessible prior to the requested release date if the DDBJ Center becomes aware that the data or accession numbers have been published in another database, web resource, or publication. The DDBJ Center notifies the submitter when sequence data are publicly released.
The DDBJ Center posts sequence data to storage and disseminates the data for public access on websites, on the NIG supercomputer, ftp sites, search tools (Search, getentry, ARSA), and application programming interfaces (APIs). For example, the DDBJ Center makes sequence data accessible for accession and text-based search on the DDBJ Center website and search. DDBJ sequence records may also be downloaded from the FTP site or accessed using the DDBJ Center’s API. SRA sequence records are available on the NIG supercomputer. SRA availability on the NIG supercomputer enables rapid access to large datasets.
Sequence data may become publicly available at different times across the DDBJ Center storage, websites, search, and analysis tools as the newly released data propagates across the system. Upon release, publicly accessible sequence data are searchable by accession number in website interfaces (Search, getentry, ARSA). The DDBJ Center also indexes the data to support text-based searches (e.g., by organism name) in websites.
In addition, the DDBJ Center exchanges sequence data with members of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC), namely the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA), European Bioinformatics Institute (EBI) at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) and the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), National Library of Medicine (NLM) at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in USA. Such exchanges enable that all INSDC sites provide access to a comprehensive collection of publicly accessible sequence data (INSDC members do not exchange sensitive controlled access human sequence data). As a result, the DDBJ Center provides public access to sequence data and metadata that are submitted to and processed by other INSDC organizations, and other INSDC organizations provide public access to sequence data and metadata that are submitted to the DDBJ Center.
Public sequence data made available by the DDBJ Center may be retrieved and redistributed by other users and presented in other websites, databases, tools, publications, curricula, conference proceedings, or other venues that are not managed by the DDBJ Center. These other resources present a snapshot from the time of retrieval and may not contain the most recent updates or changes to status.
Requesting Data Status Changes
Submitters to DDBJ and SRA are generally responsible for requesting changes to the status of their sequence data. The DDBJ Center does not directly manage the status of sequence data that are submitted to other INSDC members, and submitters to those databases must work directly with those INSDC members to change the status of data.
In certain circumstances, submitters may request that their data be removed after public release. The DDBJ Center is responsible for verifying that the request is valid (e.g., it originates from the submitter), determining whether the request meets the criteria for removal described herein, and determining the appropriate removal method.
Sequence data may be removed from public access in one of two ways: suppress or withdraw.
Data are suppressed when the submitter has concerns related to issues such as data quality or changes in the scope or timing of associated publications, and there is a need to maintain data availability via accession number to preserve the integrity of the published scientific record (see examples below). Suppressed data remain publicly accessible by accession number and are removed from indexing for text searches and API or tool retrievals (e.g., BLAST).
Data are withdrawn when there are concerns about possible harms resulting from public availability of the data such as those related to national security, privacy, or lack of proper informed consent (see examples below). Withdrawn data are not publicly accessible, even by accession number.
When data are suppressed or withdrawn, the DDBJ Center updates the status of the data and retains the data for archival purposes and to enable possible future re-release. The data status change may take effect at different times across the range of the DDBJ Center storage, websites, APIs, and analysis tools, including across other INSDC members’ resources.
Because public sequence data made available by the DDBJ Center may be retrieved and redistributed by other users and presented in other websites, databases, tools, publications, curricula, conference proceedings, or other venues that are not managed by the DDBJ Center, data that are suppressed or withdrawn may remain available through other sources that are not managed by the DDBJ Center.
Data submitters may request that suppressed data be re-released upon publication of the data or once they confirm or update questionable data.
Examples of valid reasons for a submitter to request removing sequence data include:
- Suppression of public data:
- Data reported as being from a single organism are discovered, after public release, to be contaminated with sequences from another organism.
- The taxonomic identity of the sequenced organism is determined, after public release, to be unconfirmed. For example, this may occur if there are few or no other sequences available for the organism to carry out an initial validation, and the initial designation is later determined to be incorrect and cannot be updated.
- Data are found, after public release, to contain errors that cannot be corrected, making the data unsuitable for reuse in future analysis. Errors identified by the submitter may include incorrect assembly, annotation, metadata, sample mix-up, contamination, or low-quality sequence (e.g., the submitted sequence lacks sufficient supporting evidence).
- Data are later determined to be an unallowable submission type or an erroneous submission.
- For example, DDBJ does not allow submission of another submitter’s sequence data without that submitter’s collaboration or permission. Absent that, such data can be submitted as a Third-Party Annotation (TPA) if the submitter meets TPA criteria.
- Submitters may mistakenly submit sequence data (e.g., when carrying out a trial run of the submission process).
- Data are released upon reaching the submitter-provided public release date, and before the publication or analysis referencing the data is complete.
- The submitter notifies the DDBJ Center of duplicate data in DDBJ or SRA (e.g., due to redundant submissions, or an update was provided as a new submission instead of as an update). When possible, the original accession number is added to the newer data as a ‘secondary’ accession number which results in retrieval of the new accession number for searches for the original accession number. If this tracking is not possible, typically because the submitter does not provide precise mapping from the original accession to the new accession, then the original submitted data is suppressed.
- Withdrawal of public data:
- The submitter determines, after public availability, that they did not have proper informed consent to publicly release protected human data.
- The DDBJ Center is notified (e.g., by the principal investigator, laboratory manager, institution, or journal) that that the data should be retracted based on malfeasance or fraud. the DDBJ Center will work with the complainant and/or institution to verify the claim.
- The DDBJ Center is notified that the sequence data was uploaded by a person who was not authorized to submit the data. The DDBJ Center will work with the principal investigator, laboratory manager, and/or institution to verify the claim.
- The DDBJ Center erroneously released sequence data to the public during data processing.
Data Status Definitions
Data submitted to DDBJ and SRA are assigned one of the following statuses as defined by the INSDC Status Document:
Canceled: The submitter has elected to halt the submission process for private data or the DDBJ Center has detected quality problems prior to public release. The DDBJ Center generally keeps the data temporarily to support submitters should they later decide to release the data, but the DDBJ Center may not retain data indefinitely from canceled submissions.
Private: Private data are not available publicly through any means. Data have been submitted and are undergoing processing and/or are scheduled for release at a future date. Private data are pre-decisional and confidential and may or may not become publicly released.
Public: Public data are fully accessible for search and distribution. The DDBJ Center has completed processing and publishing the data.
Suppressed: Suppressed data are data that were previously public, have been removed from the the DDBJ Center text-based search and comparative analysis results, and may be accessed only by accession number. Suppressed data often have a future date when they will return to public status (Temporarily Suppressed) or not (Permanently Suppressed).
Withdrawn: Withdrawn data are data that were previously public, have been removed from the the DDBJ Center text-based search and comparative analysis results, and cannot be accessed by the public even by accession number. The DDBJ Center retains the data to preserve the integrity of the scientific record and for disaster recovery with limited exceptions (e.g., national security).