Sequence Read Archive
Data Files
- Make sure the file names are constructed only from alphanumeral [A-Z,a-z,0-9], underscores [_], hyphens [-] and dots [.], with no whitespaces, brackets, other punctuations or symbols.
- Submit paired reads in separate fastq files (forward and reverse) in a Run. In the case of BAM, submit single BAM file which contains paired reads.
- Upload data files directly under a submission directory. Submitted archive files should NOT contain any directory structure.
- Do NOT compress BAM.
General formats
fastq
Select “fastq” for the Run filetype.
For details of the fastq format, please see NCBI website.
- Quality values must be in Phred scale. By default, 33 (!) is used for Phred quality offset. In the case of 64 (@), update the ascii_offset of Run XML to ‘ascii_offset=”@”’.
- In the DRA metadata submission web interface, technical reads (adapters, linkers, barcodes) cannot be described. If you want to desscribe technical reads, edit and submit the Experiment XML according to Formats of sequencing data files (XML examples).
- Paired reads must split and submitted using two Fastq files in a Run. Paired reads are recognized by standard read names.
- The first line for each read must start with ‘@’.
- The base calls and quality scores must be separated by a line starting with ‘+’.
- The Fastq files must be compressed using gzip.
BAM
BAM is a compressed version of the Sequence Alignment/Map (SAM) format. BAM files can be decompressed to a human-readable text format (SAM) using samtools. We recommend to submit BAM including unaligned reads as primary data.
SAM is a tab-delimited format including both the raw read data and information about the alignment of that read to a known reference sequence(s). There are two main sections in a SAM file, the header and the alignment sections, each of which are described below. Here the SAM format is explained with respect to submission of BAM files to DRA. A more comprehensive discussion of the format specifications can be found at the samtools website.
SAM Header Example:
@HD VN:1.4 SO:coordinate
@SQ SN:CHROMOSOME_I LN:15072423
UR:ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/genomes/Eukaryotes/invertebrates/Caenorhabditis_elegans/
WBcel215/Primary_Assembly/assembled_chromosomes/FASTA/chrI.fa.gz AS:ce10
SP:Caenorhabditis elegans
@SQ SN:CHROMOSOME_II LN:15279345
UR:ftp://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genbank/genomes/Eukaryotes/invertebrates/Caenorhabditis_elegans/
WBcel215/Primary_Assembly/assembled_chromosomes/FASTA/chrII.fa.gz AS:ce10
SP:Caenorhabditis elegans
@RG ID:1 PL:ILLUMINA LB:C_ele_05 DS:WGS of C elegans PG:BamIndexDecoder
@PG ID:bwa PN:bwa VN:0.5.10-tpx
SAM Alignment Example:
3658435 145 CHROMOSOME_I 1 0 100M CHROMOSOME_II 2716898 0
GCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCT
AAGCCT
@CCC?:CCCCC@CCCEC>AFDFDBEGHEAHCIGIHHGIGEGJGGIIIHFHIHGF@HGGIGJJJJJIJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJHHHHHFF
FFFCCC RG:Z:1 NH:i:1 NM:i:0
5482659 65 CHROMOSOME_I 1 0 100M CHROMOSOME_II 11954696 0
GCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCTAAGCCT
AAGCCT
CCCFFFFFHHGHGJJGIJHIJIJJJJJIJJJJJIJJGIJJJJJIIJIIJFJJJJJFIJJJJIIIIGIIJHHHHDEEFFFEEEEEDDDDCDCCCA
AA?CC: RG:Z:1 NH:i:1 NM:i:0
BAM file processing
The header and alignment section are internally consistent: each aligned read has an RNAME (reference sequence name, 3rd field) that matches an SN tag value from the header (e.g., CHROMOSOME_I), and, if provided,the alignment read group optional field (RG:Z:) is consistent with the read group ID in the header (1). It is also important to ensure that the FLAG fields (2nd field in each line) are correctly set for the data. The SRA pipeline will attempt to resolve incorrect FLAG values, but sufficiently incorrect values can lead to processing errors. The SRA does not archive optional and non-standard tags/field values contained in the alignment section. However, the entire header section of the bam file is retained. Additionally, although the SAM format allows for an equal sign (=) in the sequence field to represent a match to the reference sequence or only an asterisk (*) in both the sequence and quality fields, the DRA processing software does not recognize either of these formats.
For 10x Genomics data files, please see the GEA Single-cell submission guide.
Please note that unexpected notations used to indicated paired reads can lead to failure to recognize the pairs and an improper SRA archive (i.e. paired reads are treated like fragments). For example, using :0 and :1 at the end of the read names is atypical and is currently not recognized as an indication of read 1 and 2 in a pair. It would be better to exclude these notations and provide the two reads with the same names. Expected notations for particular platforms will work. For example, Illumina reads with /1 or /2 appended is an expected notation. Further, neglecting to set the proper bits for paired reads in the SAM/BAM flags (e.g. multi-segment template 1-bit, first segment 64-bit, and last segment 128-bit) or splitting paired reads into separate bam files can result in an improper SRA archive or failure to generate the SRA archive.
BAM file submission
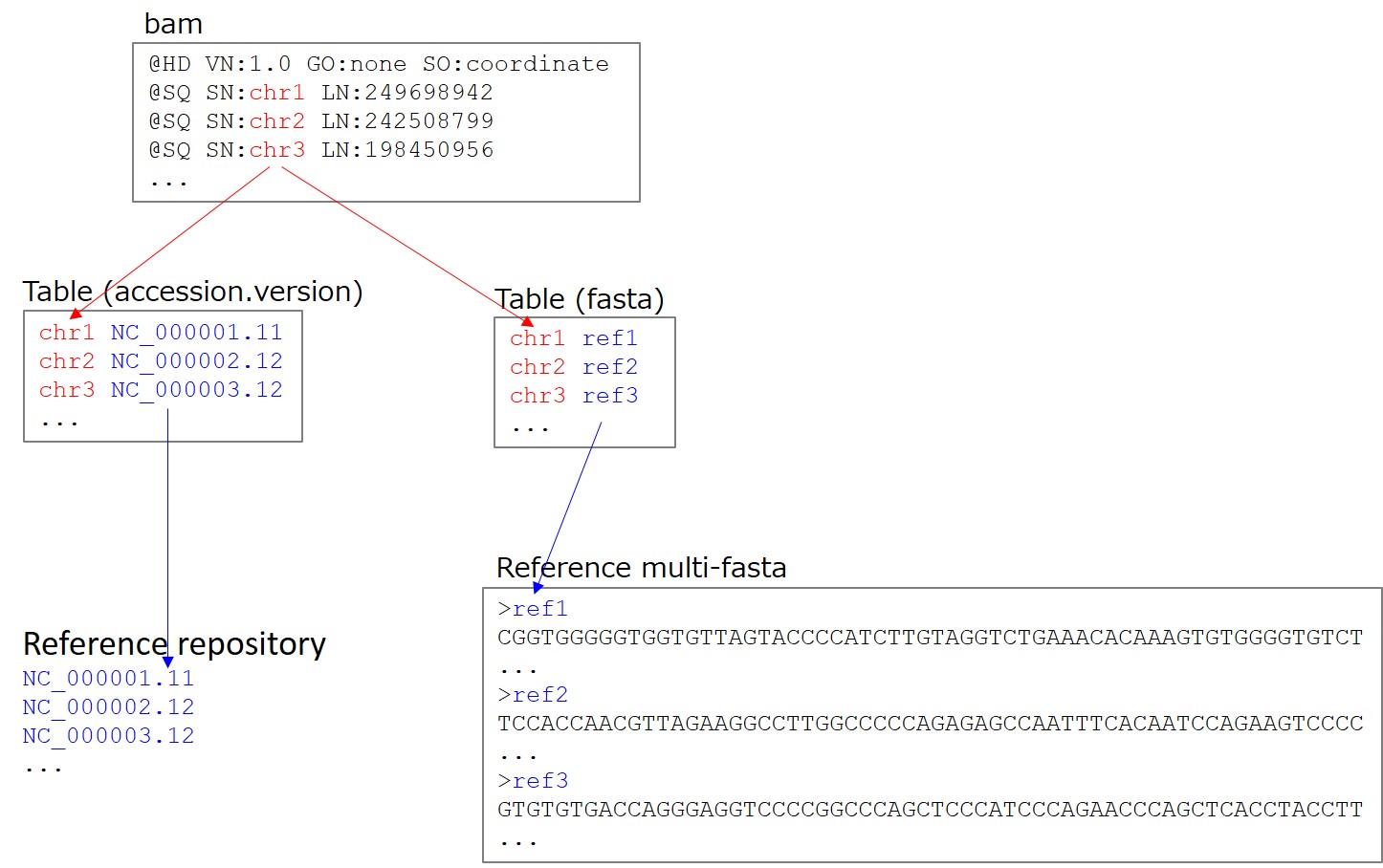
In the case of submitting alignment data, you need to submit “BAM”, “INSDC, refseq accession number OR reference multi-fasta” and “SN-reference mapping table”. Submit one bam file per Run.
An example file of the mapping table
When submitting bam file into Analysis instead of Run, the mapping table is unnecessary. However, please consider to submit bam including unaligned reads as primary data into Run.
1. BAM file submission
The alignment data can be submitted in the BAM format. The bam files should be readable by SAMtools and picard. The BAM files are nearly optimal in terms of compression and should be submitted uncompressed.
2. Specify reference by INSDC/RefSeq accession number
If references are found in https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/refseq/, references can be specified by their accession.version number (for example, NC_000001.11). Version numberis necessary. Accession numbers for references can be searched in NCBI Assembly.
3. Specify reference by supplying multi-fasta
If references are not found in https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/refseq/, submit a reference file in multi-fasta format. Select “reference_fasta” in the Run file type. The reference name in the bam header and reference sequence are linked by the name in bam header and fasta defline via the mapping table. If sequence length is different between @SQ-LN and multi-fasta, a warning is raised.
4. Specify reference by both INSDC/RefSeq accession number and multi-fasta
If a part of references are found in https://ftp.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra/refseq/, these references can be specified by their accession.version number (for example, NC_000001.11). The rest of references needs to be supplied by uploading a multi-fasta file. In the SN-reference mapping table, list accession.version numbers and sequence names of multi-fasta deflines.
5. SN-reference mapping table
A tab delimited text file describing mapping between “SN in SQ line in BAM header” and “accession OR sequence name in fasta file”. Select “tab” in the Run file type
BAM header
@HD VN:1.0 GO:none SO:coordinate
@SQ SN:chr1 LN:249698942
@SQ SN:chr2 LN:242508799
@SQ SN:chr3 LN:198450956
...
SN-fasta mapping table. In the example, the reference named ref1 in multi-fasta file corresponds to the SN:chr1.
chr1 ref1
chr2 ref2
chr3 ref3
...
Reference multi-fasta.
>ref1
CGGTGGGGGTGGTGTTAGTACCCCATCTTGTAGGTCTGAAACACAAAGTGTGGGGTGTCT
...
>ref2
TCCACCAACGTTAGAAGGCCTTGGCCCCCAGAGAGCCAATTTCACAATCCAGAAGTCCCC
...
>ref3
GTGTGTGACCAGGGAGGTCCCCGGCCCAGCTCCCATCCCAGAACCCAGCTCACCTACCTT
...
SN-fasta mapping table. In the example, the reference “NC_000001.11” corresponds to the SN:chr1.
chr1 NC_000001.11
chr2 NC_000002.12
chr3 NC_000003.12
...
Data files per sequencing platform
454
The DRA accepts sequencing run data from the 454 platform in the fastq/bam formats. Please convert output sff files to fastq/bam files.
Illumina
Submit fastq/bam files.
BGI-seq
Submit fastq/bam files.
SOLiD
Submit fastq/bam files.
Ion Torrent
Submit Ion Torrent data in the fastq format. Bam files from Ion Torrent instruments can be converted to fastq by using samtools. Converting BAM to fastq
Helicos Heliscope
Submit Helicos data in fastq created with the fixed-quality value, “14”.
Complete Genomics
Submit fastq/bam files.
Pacific Biosciences
HDF5
Pacific Biosciences uses HDF5, a container file with a directory-like structure, to store raw data. The DRA accepts both bas.h5 and bax.h5 file submissions. Note that submission of data from the RS II instrument requires one Run consists of one *.bas.h5 file and three *.bax.h5 files. Do not rename files.
bam
We support the submission of the following types of PacBio bam files. Include 1 bam file per Run. For an unaligned bam file, reference and mapping table are not necessary.
- *.subreads.bam
- *.ccs.bam
- *.reads.bam
fastq
The DRA also accepts Pacific Biosciences data in the fastq format. Select the “fastq” for the Run filetype.
Oxford Nanopore
Submit fastq/bam files.
Capillary sequencing platform
Submit capillary sequencing data in the fastq/bam format.
10x Genomics
For the 10x Genomics data files, please see the GEA Single-cell submission guide.
Analysis data files
Data files recommeded to submit as Analysis files.
PacBio Base Modification Files
PacBiosequence data also permits the analysis of methylated bases within the sequence, which can be extremely helpful to the scientific community. For example, the precise positions of those modified bases can be used to determine the specificity of the DNA methyltransferases that produced them. The PacBio analysis suite contains an analysis workflow (RS_Modification_and_Motif_Analysis) to extract these sequences and produce several files:
- motif_summary.csv
- modifications.csv
- modifications.gff
- motifs.gff
It would be beneficial to the scientific community if you were able to perform this analysis and submit at least the motif_summary.csv file for prokaryotes via as a DRA Analysis object. Please submit these files as data files of the Analysis with Sequence Annotation typein addition to sequencing reads in Run. For assistance, contact us.
NCBI guidelines of PacBio Base Modification Files
BioNano Whole Genome Map Files
BioNano mapping technology produces whole genome maps. These maps can be used in a variety of genomic analyses, including de novo assembly, structural variant detection and assembly curation. For example, BioNano physical maps can be integrated with de novo genome assemblies produced from next-generation technologies to produce high quality hybrid assemblies with increased continuity and completeness, especially in regions of genomic complexity. Files produced as part of the BioNano mapping and or hybrid assembly process include:
- CMAP
- The BioNano Genomics Irys .cmap file is a raw data view of a molecule set or assembly reporting a label site position within a genome map identified during a run. The Irys .cmap file reports the start and end coordinates and the locations of the labels on a map using a tab-delimited text based file.
- COORD
- The purpose of the .coord file is to relate the coordinates of scaffolds in a hybrid assembly to the corresponding AGP submission. The .coord file maps positions from the hybrid cmap, which may not begin or end with sequence gaps. The scaffolds are trimmed up to the leftmost label of leftmost sequence and the rightmost label of the rightmost sequence.
- XMAP
- The BioNano Genomics Irys .xmap file is a cross-comparison between two maps. The Irys .xmap file reports the comparison derived from the alignment between an anchor .cmap file and a query .cmap file. The data line displays the map start and end coordinates and the locations of the labels on the map using a tab-delimited text based file.
- SMAP
- The BioNano Genomics Irys .smap file is a description of structural variations (SV) detected between two genome maps. The Irys .smap file reports the structural variants discovered during an alignment between an anchor .cmap file and a query .cmap file. The data line displays the start and end coordinates and the locations of the SV on the map using a tab-delimited, text-based file.
- BNX
- The BioNano Genomics Irys .bnx file is a raw data view of molecule and label information and quality scores per channel identified during a run.
For the latest file specifications, please see the Bionano Genomics - Software and Data Analysis Support Materials.
If you are using BioNano data as part of your assembly generation pipeline, it would be extremely useful to the scientific community if you could submit a package comprised minimally of the molecule .bnx file and the resulting de novo assembly file EXP_REFINEFINAL1.cmap and COORD files as a DRA Analysis. We will add an analysis type and filetypes for the BioNano Genome Map files. In the meantime, please submit the BioNano files as the analysis type “De Novo Assembly” and the filetype “tsv” (Example, DRZ078181, DRZ078182).