Japanese Genotype-phenotype Archive
Submission to JGA
Submission Guide
The JGA accepts only de-identified data approved by DBCLS. The users apply for data submission to the DBCLS and the JGA will only accept submissions once the information of a successful application process has been passed from the DBCLS to the JGA.
It should be clear from the original consent agreements affiliated to your samples if your data should be subject to controlled access. All data submitted to the JGA has controlled access, which means that access to the data submitted is subject to approval by DBCLS as a part of a formal application procedure.
Controlled access does not correspond to holding a release prior to publication. All the DDBJ archival resources including the JGA enable you to hold a submission before publication.
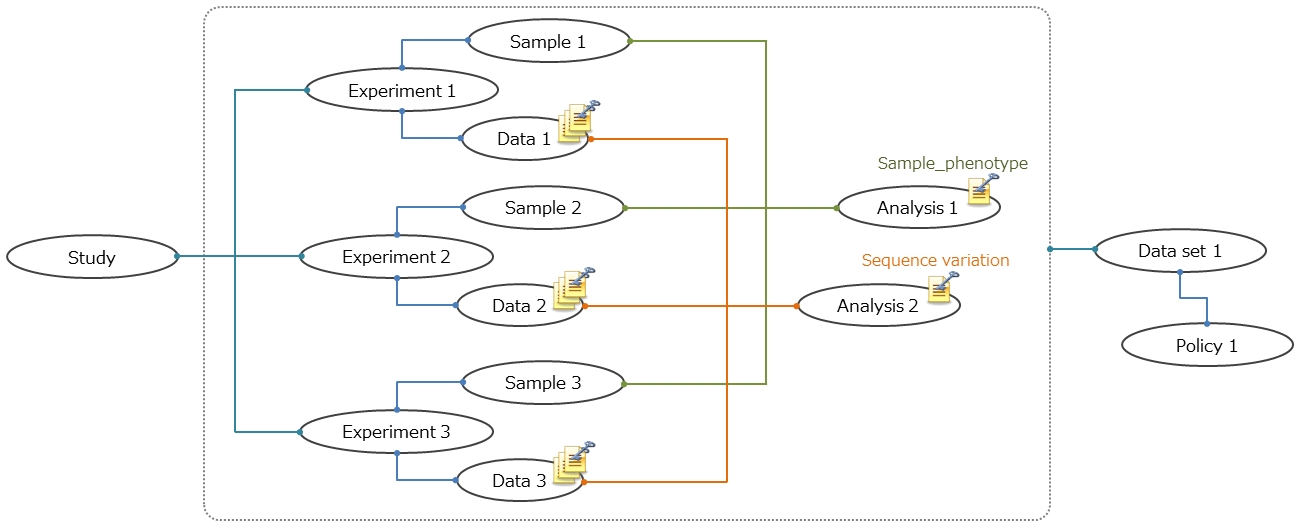
Accession numbers are issued to metadata objects with following prefixes.
| Prefix | Metadata object | Number digit | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| JGA | Submission | 6 | JGA000001 |
| JGAS | Study | 6 | JGAS000001 |
| JGAN | Sample | 9 | JGAN000000001 |
| JGAX | Experiment | 9 | JGAX000000001 |
| JGAR | Data | 9 | JGAR000000001 |
| JGAZ | Analysis | 9 | JGAZ000000001 |
| JGAD | Dataset | 6 | JGAD000001 |
| JGAP | Policy | 6 | JGAP000001 |
After creating a DDBJ account, it takes about 10 minutes for the DDBJ account becomes active in the application system.
Currently, there is no requirement for authors to use a specific JGA accession in their publications. We would recommend that authors use the JGAS (study) accession, which would provide the reader/user with a complete overview of the study and a set of links to all the data from that study.
An example of accession number citation: “Genotype data has been deposited at the Japanese Genotype-phenotype Archive (JGA, https://www.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/jga), which is hosted by the Bioinformation and DDBJ Center, under accession number JGASXXXXXX.”
Sequence data file (raw/unaligned and aligned)
Supported JGA data submission formats are described below. If you have data in any other format or have any questions please contact the JGA .
Data files should be de-multiplexed prior to submission so that each data object is submitted with files containing data for a single sample only.
BAM format
Binary Alignment/Map files (BAM) represent one of the preferred JGA submission formats. BAM is a compressed version of the Sequence
Alignment/Map (SAM) format (see SAMv1.pdf). BAM files can be decompressed to a human-readable text format (SAM) using SAM/BAM-specific utilities (e.g. samtools) and can contain unaligned sequences as well.
JGA strongly recommends to submit BAM including unaligned reads as primary data into Data.
The BAM files are nearly optimal in terms of compression and should be submitted uncompressed.
Fastq format
Primary sequence data submissions of single and paired reads are accepted as Fastq files that meet the following the requirements:
- Quality scores must be in Phred scale. For example, quality scores from early Solexa pipelines must be converted to use this scale. Both ASCII and space delimitered decimal encoding of quality scores are supported. We will automatically detect the Phred quality offset of either 33 or 64.
- No technical reads (adapters, linkers, barcodes) are allowed.
- Single reads must be submitted using a single Fastq file.
- Paired reads must split and submitted using two Fastq files. The read names must have a suffix identifying the first and second read from the pair, for example ‘/1’ and ‘/2’; (regular expression for the reads “^(.*)([\\.|:|/|_])([12])$”).
- The first line for each read must start with ‘@’.
- The base calls and quality scores must be separated by a line starting with ‘+’.
- The Fastq files must be compressed using gzip or bzip2.
Example of Fastq file containing single reads:
@read_name
GATTTGGGGTTCAAAGCAGTATCGATCAAATAGTAAATCCATTTGTTCAACTCACAGTTT
+
!''*((((***+))%%%++)(%%%%).1***-+*''))**55CCF>>>>>>CCCCCCC65
...
Example of Fastq file containing paired reads:
@read_name/1
GATTTGGGGTTCAAAGCAGTATCGATCAAATAGTAAATCCATTTGTTCAACTCACAGTTT
+
!''*((((***+))%%%++)(%%%%).1***-+*''))**55CCF>>>>>>CCCCCCC65
@read_name/2
GATTTGGGGTTCAAAGCAGTATCGATCAAATAGTAAATCCATTTGTTCAACTCACAGTTT
+
!''*((((***+))%%%++)(%%%%).1***-+*''))**55CCF>>>>>>CCCCCCC65
...
SFF format
The recommended submission format for the 454 platform is SFF.
The SFF files are nearly optimal in terms of compression and should be submitted uncompressed.
Array based (Genotypes, SNP, Expression)
The JGA accepts processed data from all types of array based technologies, such as genotypes, gene expression, methylations, etc.
We are very flexible regarding these submissions and would accept all types of files affiliated to the array experiment into the JGA Analysis.
We recommend that both raw data (CELs) and analysis files be submitted, which will enable potential users of the data to recreate your results cited in the paper as well as view the described results.
Variation data file
The JGA supports submissions of sequence variations in VCF format . The vcf files are accepted as secondary analysis object.
Other data files
Analysis can refer to multiple Data and Sample objects and summary data summarizing data files of these objects can be registered to the Analysis. Example analysis files are listed below.
- A reference sequence GFF3 file assembled by using multiple sequence files in a objects.
- A table file summarizes normalized array data files in Analysis.
Metadata
The JGA data model is created by extending the Sequence Read Archive’s model. The JGA metadata are composed of the XML objects.
JGA XML schema: JGA xsd
Summary information for public display
When JGA submissions are released, following metadata objects will be public on the JGA and DBCLS websites to display summary of submissions.
- Study:
- All fields.
- Dataset:
- All fields, number of samples, and filesize.
- Policy:
- All fields.
Submission
The submission XML is used to describe the submission transaction. It contains contact details of the submitter.
XML schema: JGA.submission.xsd
Study
The study XML describes your study in detail. It contains a title, a study type and an abstract, as it would appear in the publication. After publication, the study can be updated to include the PubMed ID of the paper containing the submitted data.
XML schema: JGA.study.xsd
Sample
The sample XML describes each of the samples used in your submission. A sample generally corresponds to a participant. Whilst the mandatory fields are minimal we highly recommend to describe the sample in as much detail as possible including subject phenotypes.
XML schema: JGA.sample.xsd
Experiment
The experiment XML is used to describe each unique set of experimental setup details. This includes the library preparation details, next generation sequencing platforms. The experiment XML can represent next generation sequencing experiments.
XML schema: JGA.experiment.xsd
Data
The data XML describes the next generation sequencing data files and their relationship with the experiments. The data XML serves as a file container.
XML schema: JGA.data.xsd
Analysis
The Analysis XML can be used to submit array data, analyzed and summarized data to JGA. Variation data can be submitted as VCF files. Only one VCF file can be submitted in each analysis and the samples used within the VCF files must be associated with JGA Samples. Optimally the VCF file would be associated with an INSDC reference assembly and sequences either by using accessions or by using commonly used labels.
XML schema: JGA.analysis.xsd
Dataset
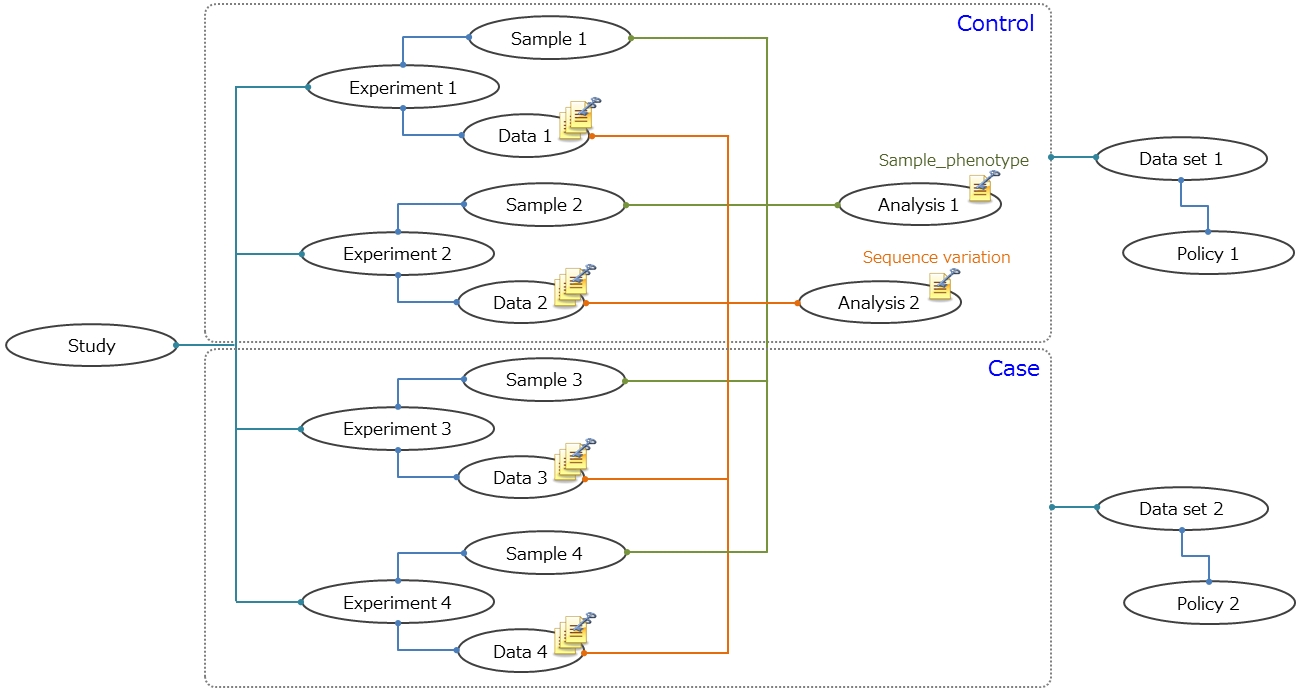
The dataset XML describes the data files, defined by the Data XML and Analysis XML, that make up the dataset and links the collection of data files to a specified Policy (Data Access Agreement). When a Study contains datasets with different policies, separate Datasets need to be created.
In general, policy is determined by informed consent with participants.
XML schema: JGA.dataset.xsd
Policy
The Policy XML describes the Data Access Agreement (DAA). If only NBDC policy is associated with a submission, submitters do not need to create a new policy.
If additional policies are needed, you need to register a policy to DBCLS and reference issued JGAP number from submitting dataset.
XML schema: JGA.policy.xsd
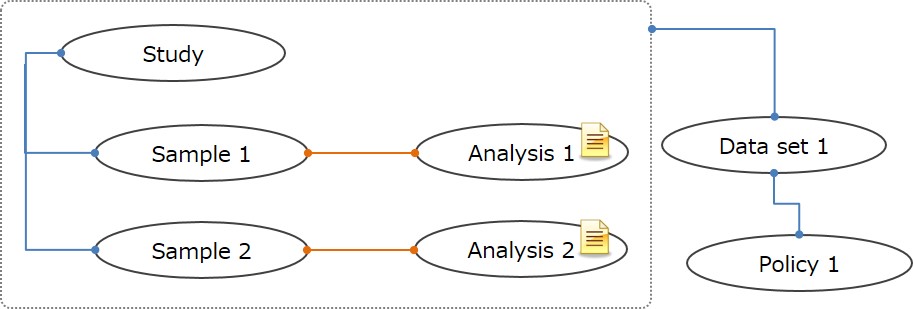
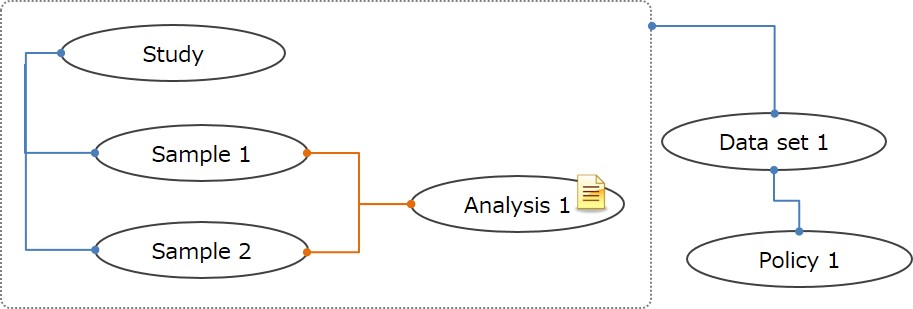
Analysis only submission
To submitting only aggregated data or data which are not suitable for Sample-Experiment-Data, these data can be submitted as Sample-Analysis instead of Sample-Experiment-Data.
To submitting Analysis only data, please contact JGA team .
Update submissions
To update your submissions, please contact to the JGA team.
If you want to add data to released Study/Dataset, you can not keep the added data private. Add data when the data can be released, or separate study to keep them private.
Data release
JGA submission is released after a hum research page is published at the NBDC Human Database.