BLAST
PROGRAM
Specify the search program from the followings.
| PROGRAM | query | Data Base | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| megablast | nucleotide | nucleotide | Aligning your nucleotide sequence with nucleotide sequence database. When you want to perform a homology search with long length of nucleotide sequence, results are provided faster than blastn program. |
|
| blastn | nucleotide | nucleotide | Aligning your nucleotide sequence with nucleotide sequence database. | |
| tblastn | amino acid | nucleotide | Aligning your amino acid sequence with nucleotide sequence database by translating database sequences taking into account all six possible open reading frames. | |
| tblastx | nucleotide | nucleotide | Aligning your nucleotide sequence with nucleotide sequence database by translating both sequences taking into account all six possible open reading frames. | |
| blastp | amino acid | amino acid | Aligning your amino acid sequence with amino acid seque nce database. | |
| blastx | nucleotide | amino acid | Aligning your nucleotide sequence with amino acid sequence database by translating your sequence taking into account all six possible open reading frames. |
Query name, Query sequence
-
Please input your sequence(s) in FASTA format.
-
You can use either “File Upload” or fill the box directly.
-
For multiple query sequence, sequence names to distinguish each sequences are indispensable. Names beginning at “>” should be placed on the first line of each sequence data (multi FASTA format).
-
If your query is one sequence, please enter the sequence. Attaching a sequence name is optional. A name beginning at “>” can be attached at the first line.
An example sequence in FASTA format
>my query sequence 1
CACCCTCTCTTCACTGGAAAGGACACCATGAGCACGGAAAGCATGATCCAGGACGTGGAA
GCTGGCCGAGGAGGCGCTCCCCAGGAAGACAGCAGGGCCCCAGGGCTCCAGGCGGTGCTG
GTTCCTCAGCCTCTTCTCCTTCCTGCTCGTGGCAGGCGCCGCCAC
Example of multiple query sequence (multi FASTA format)
>>my query sequence 1
CACCCTCTCTTCACTGGAAAGGACACCATGAGCACGGAAAGCATGATCCAGGACGTGGAA
GCTGGCCGAGGAGGCGCTCCCCAGGAAGACAGCAGGGCCCCAGGGCTCCAGGCGGTGCTG
GTTCCTCAGCCTCTTCTCCTTCCTGCTCGTGGCAGGCGCCGCCAC
>my query sequence 2
GGCCAGGGCACCCAGTCTGAGAACAGCTGCACCCGCTTCCCAGGCAACCTGCCTCACATG
CTTCGAGACCTCCGAGATGCCTTCAGCAGAGTGAAGACTTTCTTTCAAATGAAGGATCAG
CTGGACAACATATTGTTAAAGGAGTCCTTGCTGGAGGACTTTAAG
>my query sequence 3
ATGGGTCTCACCTCCCAACTGCTTCCCCCTCTGTTCTTCCTGCTAGCATGTGCCGGCAAC
TTTGCCCACGGACACAACTGCCATATCGCCTTACGGGAGATCATCGAAACTCTGAACAGC
CTCACAGAGCAGAAGACTCTGTGCACCAAGTTGACCATAACGGAC
Data Sets {#data sets}
Nucleotide (DATABASE, DIVISION)
DATABASE (Nucleotide)
Select the target database.
| nucleotide database | |
|---|---|
| DDBJ ALL | DDBJ periodical release + daily updates |
| DDBJ New | DDBJ daily updates |
| 16S rRNA | 16S rRNA from DDBJ periodical release |
| RefSeq NA | RefSeq (Genomics + RNA) |
DIVISION (DDBJ ALL/DDBJ New) {#DIVISION_DDBJ_ALL/DDBJ_New}
Check the divisions you would like to search. The following divisions
are currently available. Default selection is 10 divisions of standard
divisions (excl. SYN and ENV).
Especially for EST division, the following 21 listed organisms which
were selectted based on the submitted-number’s statistics can be
specified each other.
| Standard divisions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Human | HUM | human |
| Primates | PRI | primates other than human |
| Rodents | ROD | rodents |
| Mammals | MAM | mammals other than human, primates and rodents |
| Vertebrates | VRT | vertebrates other than human, primates, rodents and mammals |
| Invertebrates | INV | invertebrates |
| Plants | PLN | plants |
| Bacteria | BCT | bacteria |
| Viruses | VRL | viruses |
| Phages | PHG | phages |
| Synthetic DNAs | SYN | synthetic DNAs |
| ENV | ENV | environmental samples |
| High throughput divisions | ||
|---|---|---|
| HTC | HTC | High Throughput cDNAs |
| HTG | HTG | High Throughput Genomic sequences |
| TSA | TSA | Transcriptome Shotgun Assembly |
| EST divisions | |
|---|---|
| A.thaliana | Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) |
| B.taurus | Bos taurus (cattle) |
| C.elegans | Caenorhabditis elegans (nematode worm) |
| C.reinhardtii | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Chlamydomonas:green algae) |
| C.intestinalis | Ciona intestinalis (vase tunicate) |
| D.rerio | Danio rerio (zebrafish) |
| D.discoideum | Dictyostelium discoideum (soil-living amoeba) |
| D.melanogaster | D.melanogaster (fruit fly) |
| G.gallus | Gallus gallus (chicken) |
| G.max | Glycine max (soybean) |
| H.sapiens | Homo sapiens (human) |
| H.vulgare | Hordeum vulgare (incl. subspecies) |
| M.truncatula | Medicago truncatula (incl. mixed library) |
| M.musculus | Mus musculus (Mouse) |
| O.sativa | Oryza sativa (incl. subspecies rank) |
| R.norvegicus | Rattus norvegicus (incl. Rattus sp.) |
| S.lycopersicum | Solanum lycopersicum (tomato) |
| T.aestivum | Triticum aestivum (bread wheat) |
| X.laevis | Xenopus laevis (african clawed frog) |
| X.tropicalis | Xenopus tropicalis (western clawed frog) |
| Z.mays | Zea mays (maize) |
| Others | Others |
| Other divisions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Patent | PAT | patent |
| Unannotated Seq | UNA | unannotated sequences |
| GSS | GSS | genome survey sequences |
| STS | STS | sequence tagged sites |
Database Options (RefSeq)
| Release(genomic/RNA) | |
|---|---|
| Fungi | Fungi |
| Invertebrate | Invertebrate |
| Microbial | Microbial |
| Mitochondrion | Mitochondrion |
| Plant | Plant |
| Plasmid | Plasmid |
| Plastid | Plastid |
| Protozoa | Protozoa |
| Vertebrate Mammalian | Vertebrate Mammalian |
| Vertebrate Other | Vertebrate Other |
| Viral | Viral |
| Daily Updates | Daily Updates |
| Model(Genomic) | |
|---|---|
| H. sapiens | human |
| Model(RNA) | |
|---|---|
| B. taurus | cattle |
| D. rerio | zebrafish |
| H. sapiens | human |
| M. musculus | mouse |
| R. norvegicus | rat |
| X. tropicalis | western clawed frog |
Protein (amino acid)
DATABASE (protein)
| Proterin Databases | |
|---|---|
| UniProt (Swiss-Prot + TrEMBL) | Swiss-Prot + TrEMBL |
| UniProt (Swiss-Prot) | Swiss-Prot |
| UniProt (TrEMBL) | TrEMBL |
| Patent | amino acid patent data via JPO, EPO, USPTO and KIPO (When you check the “Patent”, all 4 boxes (JPO, KIPO, USPTO, EPO) was checked. If you would like to select each other, remove the unnecessary marks.) |
| DAD (periodical release + daily updates) | DAD periodical release + daily updates |
| DAD (daily updates) | DAD daily updates |
| RefSeq AA | Refseq(Protein) |
* Please check the current version is from here.
DIVISION(DAD)
Check the divisions you would like to search. The following divisions are currently available. Defauls selection is 10 divisions of standard divisions (excl. SYN and ENV). Especially for EST division, the following 21 listed organisms which were selectted based on the submitted-number’s statistics can be specified each other.
| Standard divisions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Human | HUM | human |
| Primates | PRI | primates other than human |
| Rodents | ROD | rodents |
| Mammals | MAM | mammals other than human,primates and rodents |
| Vertebrates | VRT | vertebrates other than human,primates, rodents and mammals |
| Invertebrates | INV | invertebrates |
| Plants | PLN | plants |
| Bacteria | BCT | bacteria |
| Viruses | VRL | viruses |
| Phages | PHG | phages |
| Synthetic DNAs | SYN | synthetic DNAs |
| ENV | ENV | environmental samples |
| High throughput divisions | ||
|---|---|---|
| HTC | HTC | High Throughput cDNAs |
| HTG | HTG | High Throughput Genomic sequences |
| TSA | TSA | Transcriptome Shotgun Assembly |
| EST divisions | |
|---|---|
| A.thaliana | Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) |
| B.taurus | Bos taurus (cattle) |
| C.elegans | Caenorhabditis elegans (nematode worm) |
| C.reinhardtii | Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Chlamydomonas:green algae) |
| C.intestinalis | Ciona intestinalis (vase tunicate) |
| D.rerio | Danio rerio (zebrafish) |
| D.discoideum | Dictyostelium discoideum (soil-living amoeba) |
| D.melanogaster | D.melanogaster (fruit fly) |
| G.gallus | Gallus gallus (chicken) |
| G.max | Glycine max (soybean) |
| H.sapiens | Homo sapiens (human) |
| H.vulgare | Hordeum vulgare (Barley incl. subspecies) |
| M.truncatula | Medicago truncatula(Barrel Medic incl. mixed library) |
| M.musculus | Mus musculus (Mouse) |
| O.sativa | Oryza sativa (incl. subspecies rank) |
| R.norvegicus | Rattus norvegicus (Rat incl. Rattus sp.) |
| S.lycopersicum | Solanum lycopersicum (tomato) |
| T.aestivum | Triticum aestivum (bread wheat) |
| X.laevis | Xenopus laevis (african clawed frog) |
| X.tropicalis | Xenopus laevis (african clawed frog) |
| Z.mays | Zea mays (maize) |
| Others | Others |
| Other divisions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Patent | PAT | patent |
| Unannotated Seq | UNA | unannotated sequences |
| GSS | GSS | genome survey sequences |
| STS | STS | sequence tagged sites |
DATABASE option (RefSeq)
| Release(Protein) | |
|---|---|
| Fungi | Fungi |
| Invertebrate | Invertebrate |
| Microbial | Microbial |
| Mitochondrion | Mitochondrion |
| Plant | Plant |
| Plasmid | Plasmid |
| Plastid | Plastid |
| Protozoa | Protozoa |
| Vertebrate Mammalian | Vertebrate Mammalian |
| Vertebrate Other | Vertebrate Other |
| Viral | Viral |
| Daily Updates | Daily Updates |
| Model(Genomic) | |
|---|---|
| H. sapiens | human |
| Model(Protain) | |
|---|---|
| B. taurus | cattle |
| D. rerio | zebrafish |
| H. sapiens | human |
| M. musculus | mouse |
| R. norvegicus | rat |
| X. tropicalis | western clawed frog |
Optional Parameters
SCORES
Specify how many homologous sequences are reported in list of homology
scores. Default value is 100.
When you can not find some expected data in the result of BLAST search,
it is possibly improved by using larger value for this parameter.
ALIGNMENTS
Specify how many alignments with homologous sequences are reported.
Default value is 100.
When you can not find some expected data in the result of BLAST search,
it is possibly improved by using larger value for this parameter.
EXPECT value (E-value) {#expect value}
Specify the E-value of homologous sequences in the database. Default
value is 10. If you need to get more sequences with lower homology
score, increase the “expect value”. If you need only sequences with very
high homology scores, decrease the value.
It is possible to specify it by the exponent notation. (ex: 1.0E+1)
SCORING MATRIX {#scoring matrix}
Specify the scoring matrix table for blastx, blastp and tblastn and
tblastx.
The default matrix is BLOSUM62.
| PAM30 | PAM30 substitution matrix |
| PAM70 | PAM70 substitution matrix |
| PAM250 | PAM250 substitution matrix |
| BLOSUM45 | BLOSUM Clustered Scoring Matrix |
| BLOSUM50 | BLOSUM Clustered Scoring Matrix |
| BLOSUM62 | BLOSUM Clustered Scoring Matrix |
| BLOSUM80 | BLOSUM Clustered Scoring Matrix |
| BLOSUM90 | BLOSUM Clustered Scoring Matrix |
FILTER
Specify to preform filtering (masking) of the query sequence. Default
setting of this option is “ON” (filtering is set). By using filtering,
low compositional complexity regions in your query sequence are
ignored.
For example, proline-rich regions and poly-A tails have a tendency to
coincide with an unusually high score. Although statistically
significant, such results usually reflect the structural uniqueness of
these regions and are unlikely to be biologically significant.
The query sequence is filtered by the computer program DUST of Tatusov
and Lipman in BLASTN, and by SEG of Wootton and Federhen otherwise. Low
compositional complexity regions ignored by filtering are replaced by
“N”s in the nucleotide sequence and by “X”s in the amino acid sequence.
WORD SIZE {#word size}
Specify a natural number. Default values are 28 for megablast, 11 for blastn, and 3 for the other programs.
Request ID and BLAST result
Request ID {#request id}
After pressing the “Send to BLAST” button, Request ID is displayed on the web screen. Don’t loose this ID because it is necessary for using the “Result Viewer” and/or inquiring to DDBJ for your search.
Request ID:wabi_blast_2013-0314-1407-23-16-946732
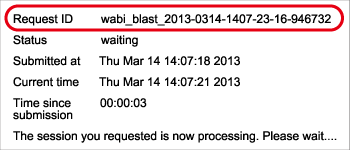
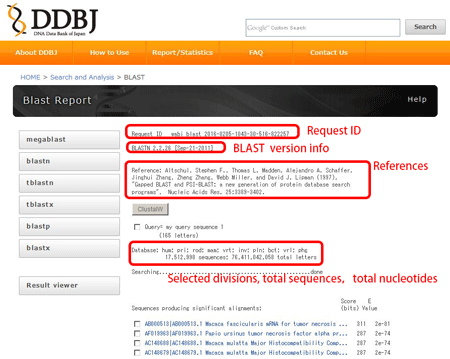
Information contained in the result screen {#result screen}
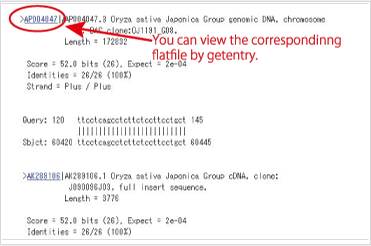
View the flatfile of the entries {#view flatfile}
Select the accession numbers, and prres the “getentry”button. You can view the flatfile of the sequences in the getentry.
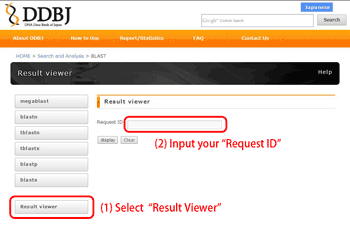
Result Viewer {#result viewer}
You can view your result using “Request ID” at any time (within the
retention period).
The results will be deleted after 7 days.
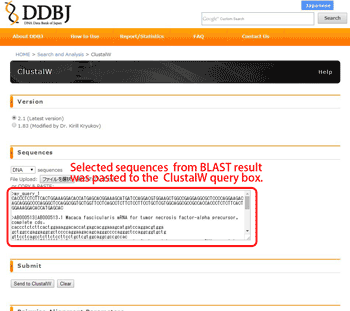
ClustalW Set up
Select the sequences which you would like to suceed the clustalW, then press the “ClustalW” button. Your selected sequences are automatically pasted in the ClustalW query box.
1.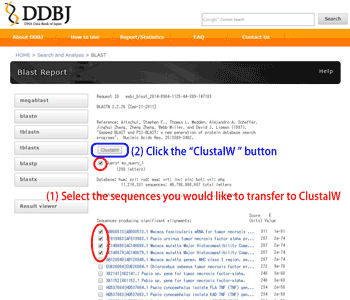 2.
2.
Reference
Original Articles
- Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ. (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25(17):3389-3402.
Related Articles
- Zhang J, Madden TL. (1997) PowerBLAST: A New Network BLAST Application for Interactive or Automated Sequence Analysis and Annotation. Genome Res.7(6):649-656.
- Madden TL, Tatusov RL, Zhang J. (1996) Applications of network BLAST server. Methods Enzymol. 266:131-141.
- Gish W, States DJ. (1993) Identification of protein coding regions by database similarity search. Nat Genet. 3(3):266-272.
- Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 215(3):403-10.
- Karlin S, Altschul SF. (1990) Methods for assessing the statistical significance of molecular sequence features by using general scoring schemes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 87(6):2264-2268.
BOOK {##reference_list}
- [BLAST] Ian Korf, Mark Yandell and Joseph Bedell, OREILLY