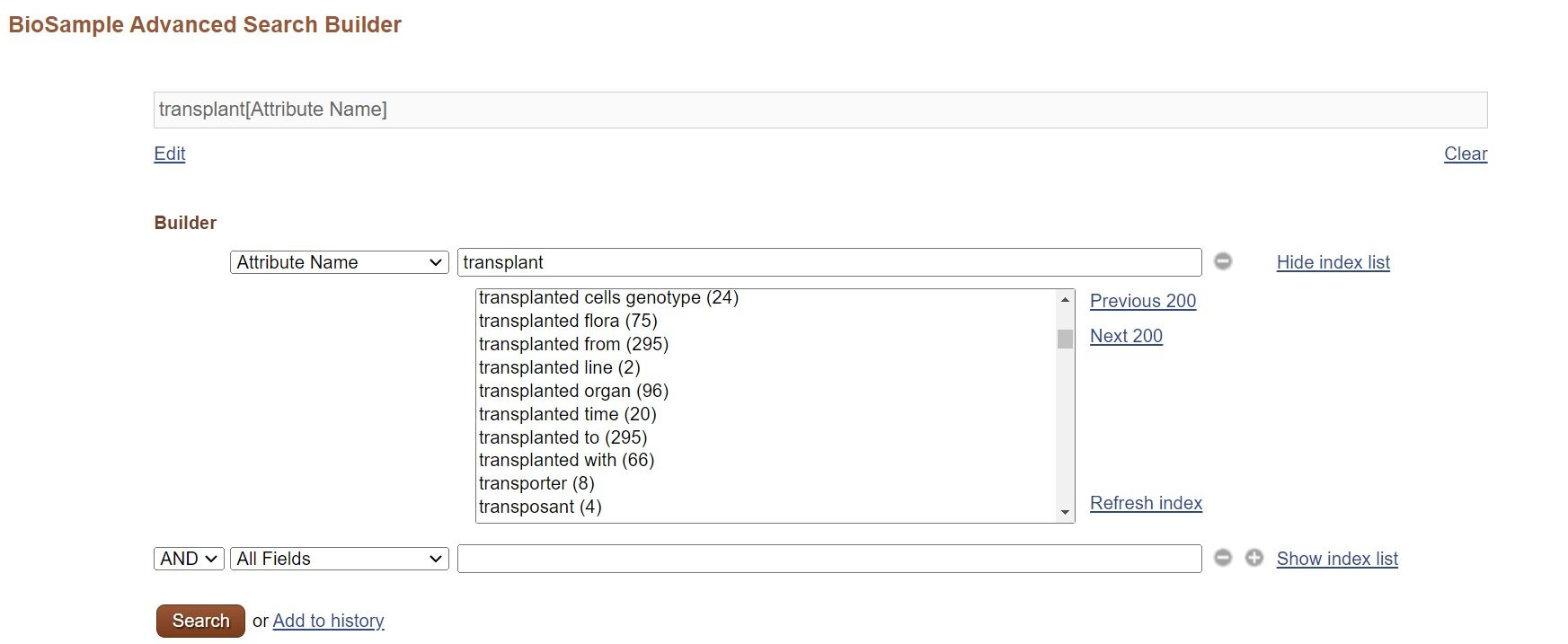
FAQ
-
When there are many Experiment and Run objects, create metadata XMLs by using the excel for the DRA metadata and the XML generator. The metadata can be registered by uploading the Submission/Experiment/Run XMLs in D-way. Please see Submit metadata by the excel for details.
-
Barcoded data files should be demultiplexed prior to submission and a unique BioSample should be created for each barcoded sample; in other words, each BioSample must be linked to one or more unique data files.
If necessary, describe relationship between barcode sequences and samples in the Library Construction Protocol of Experiment as free-text.Regarding 10x Genomics data in which samples tend to be large number, please see the GEA Single-cell submission guide.
For details, see Data Files.
-
How to deal with validation errors in the DRA submission?
- Sequencing data
- DRA
Make Sra Error
constraint violated while executing function within virtual database module
Read names are possibly not unique in Run.
Please see the FAQ: How are my data files processed? and revise duplicated read names if there.path not found while accessing directory within file system module - no message text available
Files are not recognized. This error occurs in the following cases:
- filename contains whitespace
- files are in sub-directories
- fastq files are tar archived
CheckSum Error
The MD5 values in the Run metadata (Expected MD5) are different from those of the uploaded files (Uploaded MD5). Please check the followings.
Check whether the MD5 values of the files in your local computer match those entered in the Run metadata or not.
- If the MD5 values in the Run metadata are not correct, revise the values in the metadata.
- If those values match, corresponding uploaded files may be corrupted during file transfer, so please re-upload the files.
File Name Error
Undefined or File not found: @SQ SN:
Please upload the SN-reference mapping table files to the directory.
See the Data Files for details.Metadata XML registration
When registering metadata XML files whose SPOT_DESCRIPTOR elements have been added or modified, following errors may occur.
Reads having no application read
Read composition
Read Index : 0 1 Read : ATCCGG CATCAGTTGAT………………………………………………… Base Coordinate : 1 750Read Type : Primer Linker (should have at least one application) Reads with inconsistent base coordinate
Read 1 composition
Read Index : 0 1 Read : ATCCGG…………… CATCAG…………… Base Coordinate : 1 1 (should be > 1) Read Type : Forward Reverse Read 2 composition
Read Index : 0 1 2 Read : TCAG ATAGAGTTG……… TCGTATAACTTCGTATAATGTATGCTATACGAAGTT Base Coordinate : 1 5 4 (should be > 5) Read Type : Adapter Forward Reverse Read 3 composition
Read Index : 0 1 Read : ATCCGGGTGTGTCATCAG CATCAG…………… Base Coordinate : 2 (should start at 1) 19 Read Type : Adapter Forward Reads with relative order which cannot be specified
Read composition
Read Index : 0 1 2 3 Read : TCAG ATAGA…………… ………………… CTCAT………………………………………………………… Base Coordinate : 1 5 Read Type : Adapter Forward Linker Forward (This forward cannot be specified) Spot (Read Spec) metadata
Read Index Read Class Read Type Ordering Method 0 Technical Read Adapter BaseCoord = 1 1 Application Read Forward BaseCoord = 5 2 Technical Read Linker RelativeOrder 3 Application Read Forward RelativeOrder -
Why is reads number of fastq less than that of SRA file?
- Downloading files
- DRA
The DRA generates fastq files from the raw data SRA files by using the fastq-dump in the NCBI SRA Toolkit with following options.
fastq-dump -M 25 -E --skip-technical --split-3 -W <SRA file>- -M 25: Minimum read length to output is 25 (default is 25)</li>
- -E: No sequences starting or ending with >= 10N</li>
- –skip-technical: Dump only biological reads</li>
- –split-3: Legacy 3-file splitting for mate-pairs: first and second biological reads satisfying dumping conditions are placed in files *_1.fastq and *_2.fastq, respectively. If only one biological read is present, it is placed in *.fastq.</li>
- -W: Apply left and right clips</li>
Reads are filtered and trimmed according to above dumping conditions, reads number of fastq is generally less than that of SRA file.Users can generate unfiltered and untrimmed fastq files by using following fastq-dump options.
fastq-dump -M 1 --split-3 <SRA file> -
How do I access public DRA data?
- Downloading files
- DRA
You can access the public DRA data through https/ftp and in the NIG supercomputer.
You can retrieve the filepath by searching accession numbers in the DDBJ Search.- https: https://ddbj.nig.ac.jp/public/ddbj_database/dra
- ftp: ftp://ftp.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/ddbj_database/dra
- ascp: anonftp@ascp.ddbj.nig.ac.jp:/ddbj_database/dra
- Supercomputer: /usr/local/resources/dra
https
Access through your web browser.
Examples:
DRR000001 fastq- https://ddbj.nig.ac.jp/public/ddbj_database/dra/fastq/DRA000/DRA000001/DRX000001/DRR000001.fastq.bz2
- https://ddbj.nig.ac.jp/public/ddbj_database/dra/fastq/DRA000/DRA000001/DRX000001/DRR000001_1.fastq.bz2
- https://ddbj.nig.ac.jp/public/ddbj_database/dra/fastq/DRA000/DRA000001/DRX000001/DRR000001_2.fastq.bz2
DRR000001 sra
- https://ddbj.nig.ac.jp/public/ddbj_database/dra/sra/ByExp/sra/DRX/DRX000/DRX000001/DRR000001/DRR000001.sra
ftp
Download files by wget etc.
Examples:
DRR000001 fastqwget ftp://ftp.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/ddbj_database/dra/fastq/DRA000/DRA000001/DRX000001/DRR000001.fastq.bz2 wget ftp://ftp.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/ddbj_database/dra/fastq/DRA000/DRA000001/DRX000001/DRR000001_1.fastq.bz2 wget ftp://ftp.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/ddbj_database/dra/fastq/DRA000/DRA000001/DRX000001/DRR000001_2.fastq.bz2DRR000001 sra
wget ftp://ftp.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/ddbj_database/dra/sra/ByExp/sra/DRX/DRX000/DRX000001/DRR000001/DRR000001.sraascp
Installing Aspera and install the aspera.
To download data, please see How to use Aspera.Supercomputer
You can direcly access the public data at /usr/local/resources/ in the General Analysis Section of the NIG supercomputer.
Examples: Copy DRR000001 fastq files to your home directory.
cp /usr/local/resources/dra/fastq/DRA000/DRA000001/DRX000001/DRR000001.fastq.bz2 ~/ cp /usr/local/resources/dra/fastq/DRA000/DRA000001/DRX000001/DRR000001_1.fastq.bz2 ~/ cp /usr/local/resources/dra/fastq/DRA000/DRA000001/DRX000001/DRR000001_2.fastq.bz2 ~/ -
How do I add reference information?
- Update
- BioProject
- BioSample
- DDBJ
- DRA
Please provide the PubMed ID (recommended) or DOI as the paper information in the form below.
Database Example of Accession Reference information section How to update DDBJ AB12345678
ABCDEF010123456Flat file Application Form for DDBJ Update DRA DRR000001 BioProject referenced by DRA Application Form for BioProject/BioSample/DRA Update GEA E-GEAD-1 GEA Metadata IDF
BioProject referenced by GEAApplication Form for GEA Update MetaboBank MTBKS1 MetaboBank Metadata IDF Application Form for MeatboBank Update BioProject PRJDB1 BioProject Application Form for BioProject/BioSample/DRA Update BioSample SAMD00000001 Depend on the database where experimental
data obtained from samples is registered.Application Form for BioProject/BioSample/DRA Update -
How should I cite DRA accession numbers in publications?
- Accession number
- DRA
Please cite accession numbers according to instructions of submitting publications.
Example citation
Nucleotide sequence data reported are available in the DDBJ Sequenced Read Archive under the accession numbers DRXxxxxxx and DRXxxxxxx. -
When our paper was published, what should I do?
- Update
- DDBJ
Contact us from this form with “Our paper was published” in [Subject].
-
What is the relationship between BioSamples, SRA Experiments, Runs and my data files?
- Metadata
- BioSample
- DRA
BioSample is descriptive information about the biological source materials, or samples, used to generate experimental data in any of primary data archives.
Please see Sample granularity.Each SRA Experiment is a unique sequencing library and sequencing method for a specific sample. Importantly, much of the descriptive information that is displayed in the public record of your data is captured at the level of the DRA Experiment.
SRA Runs are simply a manifest of data file(s) that should be linked to a given sequencing library – no information present in the Run is displayed on the public record of your project.
Note that all data files listed in a Run will be merged into a single SRA archive file (and fastq file for distribution). -
What is an MD5 checksum and how do I compute it?
- Sequencing data
- DRA
MD5 checksums are used by DRA to verify integrity of transmitted data.
MD5 checksum is a 32-character alphanumeric string (example: bf4ac50dcd58bd2860dfac48c7fca348).
Please refer to the this page. -
Can not find appropriate feature key
- Submission
- DDBJ
See Definition of Feature Key and Feature Table Definition.
When you can not find any accommodated feature, use misc_feature and enter information in value of /note qualifier.For instance, since DDBJ is a database for nucleotide sequences, we do not prepare any specific item for amino acid sequence motifs.
However, you can describe such kind of information by using misc_feature with /note qualifier. -
DDBJ only accepts update requests from submitters of the data except publication reference update.
If you are not the submitter you will need permission from the submitter before requesting update.
See Rights and Duties of SubmitterDDBJ can forward your comments to the submitter.
Please Contact us by selecting “Inquiry to the sequence submitters”. Please note that we can not guarantee any response from the submitter.
-
We only accept the request from the original submitter of the entry.
Please contact us from Contact by selecting the item, “Updating Submitted Data” with accession numbers. -
Can I update submitted data by using the DDBJ Nucleotide Sequence Submission System?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
Because the DDBJ Nucleotide Sequence Submission System is for new submissions, you can not update submitted data.
For update, see Data Updates/Corrections. -
I would like to know the correspondence of accession numbers and private sequences
- Accession number
- DDBJ
Please contact us from contact form by selecting the item “NSSS” or “MSS” with following items.
- E-mail address of contact person
- Accession numbers or EntryIDs
We will answer about your data.
-
When our paper was accepted, what should I do?
- Update
- DDBJ
Contact us from this form with “Our paper was accepted” in [Subject].
-
How to postpone the hold date?
- Update
- DDBJ
Contact us from this form by selecting “Change the hold-date” in [Subject].
-
Contact us from this form with “Change description about the contact person” in [Subject].
-
How to update our sequence?
- Update
- DDBJ
Please send your request to DDBJ with the following contents in clear English.
To :
- Accession numbers:
- The modified part:
- Total base count:
- Other modified feature:
- Updated sequence in full length: Please use the following format.
>AB******1 aaaaaaaaaattttttttttggggggggggccccccccccaaaaaaaaaatttttttttt ggggggggggccccccccccaaaaaaaaaattttttttttggggggggggcccccccccc // >AB******2 aaaaaaaaaattttttttttggggggggggccccccccccaaaaaaaaaatttttttttt ggggggggggccccccccccaaaaaaaaaattttttttttggggggggggcccccccccc aaaaaaaaaat //- Header line; starts with “>”, followed by the accession number at the head of each sequence.
- Sequence; each line must be 60 letters or less.
- End line; end flag, “//”, must be at the end of each sequence.
-
Can I see history of the sequence record?
- Search
- getentry
You can see revision history of the sequence record by using gethistory. Please see getentry HELP.
-
If you are making update request for large number of entries, or many changes of features/locations/qualifiers due to sequence modification, see followings.
- (1) Update information is in common of all entries.
- Example: change reference or submitters information, postpone the hold-date, etc..
In principle, send your request via DDBJ Update Form
- (2) Contents of corrections are different among entries.
- Example: change each clone or gene name of all entries, etc..
- (3) Extensive correction of data
- Example: change more than 30 features due to the sequence update, etc..
In case of (2) or (3), we would like to know the number of entries, the correction item, etc. to specify the file format for your request.
Contact us in advance from DDBJ Update Form by selecting ‘Update data contents’.
In general, we handle update requests within several days but for a large number of entries, it might take us time in updating the data.
Be sure to contact us beforehand when you request the release of data which accompanies correction. -
DDBJ does not provide a method for limited disclosure via password authentication or similar means.
When you have to show your sequence with private (“Hold-Until-Published”) status for only particular individuals, you can send sequences in a text file.
If the reviewer wish to confirm the condition and/or the descriptions of your sequence submission, you can choose either of the following two procedures;- a) Publish your sequences through DDBJ.
- If you do not mind to open your sequences to the public, please send us your request to publicize your submitted sequences with all of accession numbers.
- b) Send DDBJ flat files of your submission to the reviewer
- When the submitter requests to us, we send the text file including DDBJ flat files to the submitter. So, please send us your request with all of accession numbers to get DDBJ flat file(s) of your submission. Then, you can forward the text file to the reviewer.
Contact us from Contact if necessary.
For DRA/GEA/JGA submissions, please see How to provide my private data to journal reviewers?.
-
Why is the retracted data still available?
- Search
- DDBJ
For once published data, we can restrict use of the data if conditions are met. Please see DDBJ and SRA Data Processing for details.
In case of the use restriction, DDBJ will not include the restricted data in periodical releases and remove from all services of DDBJ.
However, the data is permanently available on getentry if queried by its accession number. This rule is not applied when the data is published by any mistake of INSD. This policy is documented in “Nucleotide Sequence Database Policies” as follows;
All database records submitted to the INSD will remain permanently accessible as part of the scientific record. Corrections of errors and update of the records by authors are welcome and erroneous records may be removed from the next database release, but all will remain permanently accessible by accession number.
In addition, there are third-party databases using INSD data. We can not support to delete data of these databases. If you are to delete the cited data of third-party databases, you have to contact the relevant database.
Reference: INSDC Status Document
-
DDBJ does not accept any reservation for updating sequence data.
Therefore, in case of updating published data, the data will be immediately re-distributed after update.Please select either of following ways.
- In this time, canceling the request for update, when you can publish updated data, contact us again.
- Submit the updated data as a new data with hold
date. When the new data is
published, the accession number of the old data will become a
secondary accession number for the new data.
# Please inform us during submitting the new data to link it to the old data.
-
How to restore released data to private?
- Update
- DDBJ
- DRA
For sequence data processing and status at DDBJ and DRA, please see DDBJ and SRA Data Processing.
DDBJ
In principle, DDBJ can not restore any published data.
See also following item about Suppressed.In principle, you cannot remove your sequence data from getentry, if it has already been open to the public (If DDBJ wrongly published your data because of any mistakes, the data should be removed as soon as possible).
However, if there is some specific reason for removing your sequence data (i.e. some error is found, etc.), we can change your sequence data to Suppressed so that the data to be removed from keyword and sequence similarity searches.
Please send your request from DDBJ Update form with the following contents.
- Accession numbers:
- Reason in brief:
- New hold-date: (e.g. 2019/06/25)
If we restrict access to your sequence data and remove it from the public view, then it will no longer be included in homology search services at DDBJ or distributed as a part of the next DDBJ periodical release. However, it may remain in other third party databases, and will still be retrievable in getentry by accession number based queries.
Moreover, our unified database may be copied and redistributed without permission at any other organizations. In case you need to withdraw your entry from such database, we ask you to make request directly to the organization which manages the database.
- References
- DDBJ and SRA Data Processing
- Why is the retracted data still available?
- INSDC Status Document
DRA
Contact the DRA team to change public DRA data to Suppressed.
-
How to delete my data?
- Update
- DDBJ
In principle, following two conditions are required to delete your sequence data;
- The sequence data has not yet been publicized
- The accession number of the data has not yet been published.
Please send your request from DDBJ Update with the following contents in clear English.
- Accession numbers:
- Reason in brief:
Just for information, we can restrict access to your sequence data that have been open to the public, if the conditions are met.
See also the following item. -
Can not find the sequence data, though the accession number cited on a paper.
- Accession number
- DDBJ
DDBJ releases sequence data submitted with a hold date according to Principle of “Hold-Until-Published” data release.
Please confirm if the ID on the paper is Accession Number Assigned by INSD or not.
If accession numbers on the paper, please contact us from contact form by selecting the item, “Updating Submitted Data” with following items.
- Accession numbers on the paper
- Title of the paper
- Authors
- Journal name
- Volume, pages, year
- DOI, PubMed ID, URL
-
What is the search service that the latest data are available at the earliest period?
- Search
- getentry
It is getentry.
“getentry” is a system for data retrieval by accession numbers, etc.
In general, the sequence data will be available on getentry from the day after processed to release. -
What kinds of data are acceptable at DDBJ?
- Submission
- DDBJ
See Databases and Data Submission Systems and Categories for Sequence Data.
If you are not sure to which category your sequence data should be submitted, use Submission navigation.
See the following sites for detail and relationships of data types.- Data Submission from Genome Project
- Data Submission from Transcriptome Project
- Division
- Categories of Annotated/Assembled Data
If you still have any question, please contact us from Contact.
-
How to submit only annotation for previously reported sequences?
- Submission
- DDBJ
If your annotation meets the requirements of TPA Submission Guidelines, DDBJ can accept it as TPA (Third Party Data).
-
How to submit sequence data with annotation to DDBJ?
- Submission
- DDBJ
Select from following two ways.
- DDBJ Nucleotide Sequence Submission System (NSSS): an interactive application to enter all of items via web form
- Mass Submission System (MSS): to send submission files to DDBJ, directly
In general, we recommend to use NSSS.
However, since NSSS can not accept all types of sequence data, it may be required to use MSS for your data submission.
See Workflow of the data submission to DDBJ -
How to submit amino acid sequences?
- Submission
- DDBJ
In general, you can submit amino acid sequences by describing CDS feature for your nucleotide sequences.
However, DDBJ does not accept amino acid sequences only, i.e. without any nucleotide sequences.
In that case, please submit to UniProt, directly.
You can submit amino acid sequences to UniProt through SPIN.
Please contact to datasubs@ebi.ac.uk. -
How to submit assembled EST sequences?
- Submission
- DDBJ
DDBJ can not accept only assembled EST sequences. However, DDBJ can accept EST assembled sequences as TSA with original (i.e. before assemble) sequence data. See also Data Submission form Transcriptome Project.
When original sequence data (primary entries) are generated from Next Generation Sequencers, submit to DDBJ sequence Read Archive (DRA), from traditional sequencers, submit as EST via Mass Submission System (MSS).
Then, DDBJ can accept assembled sequences (both de novo and reference mapping) as TSA through MSS. -
See Organism qualifier.
For detail, see either of following cases;2. In case of unidentified species names, proposing a new species etc.
3. environmental sample -
In cases of sequences derived by direct molecular isolation from soil, sea water, etc. i.e. a bulk environmental DNA sample by PCR with or without subsequent cloning of the product, DGGE, or other anonymous methods, see What is ENV ? – environmental samples.
For description of organism qualifier, see 3. Environmental samples.Though frequently confused, the term, ‘environmental samples’, does NOT mean “wild type”. If sequences are derived from isolated or cultured organisms, the sequence data are not classified into environmental samples.
-
For description of organism qualifier, see 4. Artificially constructed sequences.
-
How to describe the evidence of speculation for the feature?
- Submission
- DDBJ
You can use experiment or inference qualifier to describe evidence of speculation in each feature.
-
Should we send offprint related to our sequence data?
- Update
- Submission
- DDBJ
Generally, DDBJ do not need any offprint to process your data.
Occasionally, DDBJ may contact the submitter of sequence data to ask sending an offprint, if necessary. -
When you kindly describe about using DDBJ on academic papers etc., in general, please use the latest article for DDBJ on Nucleic Acids Res. Database issue as a reference.
However, please note followings.
- In case of citation for each sequence record
- In general, it is enough to describe accession number for it in your publication.
If you discuss about the data in detail, please use primary citation for the data as a reference. In case of citation for each service provided at DDBJ - In general, please use original article for each service as a reference.
-
Basically, please submit every sequence that you have experimentally determined, whatever the resource of genome, mRNA or any others.
In principle, DDBJ accepts submission of experimentally determined sequence in its contiguous structure.
You can describe mRNA feature, CDS feature and so on as annotation for genomic sequence, however, descriptions of mRNA features do not mean “the mRNA sequence is experimentally determined.”, in general.
If you have read mRNA sequences, please submit mRNA sequences to DDBJ. See also Acceptable data for DDBJ. -
Yes you can. It ought to be required at ‘instructions to authors’ of most of journals to submit sequence data to DDBJ (, EMBL-Bank or GanBank) before the paper submission.
During submission of sequence data, select status for your REFERENCE as follows.- “Unpublished”; In cases of preparing paper, during paper submission, or you do not prepare any publication.
- “In Press”; When your paper is accepted and in press.
Your citations will be appeared at REFERENCE 2 or after on DDBJ flat file.
-
Regardless you are to publish academic paper or not, DDBJ accepts your submission of sequence data.
If you have no plan to paper publication, you have to fill following items of REFERENCE.- status: [Unpublished]
- year: tentative year (this year), i.e. 2014
- title: tentative title to explain your data
- ab_name (authors): abbreviation of tentative author(s) (often the same as ab_name of SUBMITTER)
When you change your plan after sequence data submission, i.e. if you publish a paper, contact us from this form to send request with subject “Our paper was published”.
-
Do we have to submit sequence data to DDBJ, when the journal has no requirement to do so?
- Submission
- DDBJ
Though there is no requirement to submit sequence data to DDBJ (, EMBL-Bank or GenBank) on the journal, we strongly recommend to submit sequence data to DDBJ for improvement of data availability for readers of your paper.
-
Is it OK to submit sequence data by only one submitter?
- Submission
- DDBJ
DDBJ accepts updating requests only from the original submitter of the entry.
Basically, we strongly recommend to describe joint submitters more than two persons, e.g. at least a true worker and an adviser, to avoid lost communication in future. -
Should I submit sequence data to GenBank?
- Submission
- DDBJ
When sequence data are published, the data will be shared among DDBJ, ENA and GenBank. So, it is necessary and sufficient to submit sequence data to either of three data banks only once.
If you submit sequence data to GenBank after submission of the same data to DDBJ, the data will be duplicated. So, do not submit the same data to two or more data banks.Though some journals instruct to authors to submit sequence data to GenBank, Accession Number is commonly used by all of DDBJ, ENA and GenBank to construct INSD.
-
Should I submit sequence data to GenBank?
- Submission
- DDBJ
When sequence data are published, the data will be shared among DDBJ, EMBL-Bank and GenBank. So, it is necessary and sufficient to submit sequence data to either of three data banks only once.
If you submit sequence data to GenBank after submission of the same data to DDBJ, the data will be duplicated. So, do not submit the same data to two or more data banks.Though some journals instruct to authors to submit sequence data to GenBank, Accession Number is commonly used by all of DDBJ, EMBL-Bank and GenBank to construct INSD.
-
Can we submit sequence data related to patent application?
- Submission
- DDBJ
Nucleotide sequence data related to patent applications are transferred from Japan Patent Office to DDBJ.
So, usually, you do not have to submit such sequence data to DDBJ.However, if you apply to any other Patent Office, or if you need to publish a paper during patent application, confirm at Patent Office whether you can submit the data to DDBJ or not.
Note that when the sequence data is published from DDBJ, the data becomes a part of the public domain, as “official notice”.
References
-
If you submit nucleotide sequence data to DDBJ, you can get NO priority for the data.
DDBJ takes no responsibility for any property or priority issues for patenting. For patent application, you should confirm JPO or some other Patent Offices. -
If I submit sequence data with gene and protein names, will the names become official?
- Submission
- DDBJ
DDBJ does not have any right for the gene nomenclature. Also, DDBJ does not make any official collaboration with any committee of gene nomenclature. If there is no particular incident, the descriptions related to gene nomenclature are described as provided by submitter.
Even if you name a gene during your sequence data submission to DDBJ, there is no guarantee that the gene name is accepted at research communities.- References
- Gene nomenclature at DDBJ
You should confirm each gene nomenclature committee, i.e. HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) for human, MGI - Mouse Nomenclature for mouse, and so on.
-
How to submit sequence data related to DNA polymorphism?
- Submission
- DDBJ
-
In general, you can describe base substitutions by using variation feature with /replace and /note qualifiers.
In case of using DDBJ Nucleotide Sequence Submission System, select ‘other’ for template.
About format of feature annotation, see F01) polymorphism and variation at Description Examples of Sequence Data. -
Will SNP data submitted to DDBJ be automatically reflected in dbSNP?
- Submission
- DDBJ
- TogoVar
SNP data submitted to DDBJ is not reflected in dbSNP.
For information on the submission format to DDBJ, please refer to the Description Examples of Sequence Data, section F: Variation, as well as Representative submissions of identical sequences for variation studies.TogoVar-repository accepts human SNP data. Although data exchange with the NCBI dbSNP is planned, it has not yet been implemented. Therefore, SNP data registered to TogoVar-repository are not reflected in dbSNP.
Please also refer to FAQ “Where to submit variant data, such as Single Nucleotide Variants (SNVs), Copy Number Variants (CNVs) and structural variants?” -
For instance, when the length of sequence is 199035 bp and a CDS feature is located in the range from 199001 to 100, you should describe the location of CDS feature as
join(199001..199035,1..100)
See also Description of Location in detail. -
To submit a complete sequence of a genome, are annotation data for the genome required?
- Submission
- DDBJ
As feature annotation, we strongly recommend you to describe CDS (protein-coding sequence),rRNA,tRNA and so on.
Please inform us in detail, when you apply to Mass Submission System. -
When the correspondences between nucleotides and amino acids are different from the standard genetic code, how to describe CDS feature?
- Submission
- DDBJ
At first, please confirm whether The Genetic Code is appropriately selected or not.
Generally, if /transl_table qualifier is appropriately described with a number of the genetic code, the nucleotide sequence is automatically translated to amino acid sequence according to the genetic code.In exceptional cases of specific codons (selenocysteine etc.) that is not followed the genetic codes, describe /transl_except qualifier, appropriately.
In cases of RNA editing, ribosomal frameshift or mitochondrial TAA stop codon, see Description Examples of Sequence Data and describe with either of qualifier(s), /exception and /translation, /ribosomal_slippage or /transl_except, respectively.
In case of rare initiation of translation, staring with an amino acid other than methionine, describe the location of CDS feature with starting from “<”, operatively indicating 5’end not complete.
And describe brief explanation about the translation mechanism in /note qualifier. -
Who should be the Contact person?
- Submission
- DDBJ
See Contact person.
If your affiliation was changed after sequencing or when you belong two or more institutes, please describe the most responsible one as a representative. -
How to describe a submiter or an author who has first name only?
- Submission
- DDBJ
- In case of Mass Submission System
- Describe first name, only.
Though some warning will be outputted, please ignore them. - In case of Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- Please enter first name with some dummy initial.
Please inform us about the person with “Submission Information” on Final confirmation screen
-
How to contact the submitter of sequence data?
- Contact form
- DDBJ
Since 2007, we have removed E-mail addresses and phone numbers from sequence data.
If you can find a related paper at REFERENCE on DDBJ flat file, contact information would be available on the paper.
When you wishes to contact to the submitter(s) of an entry of your interest, please select “Inquiry to the sequence submitters” in Contact with reasons briefly, then we will forward your message to the submitter(s). -
I have not yet received accession number, how many days does it take to get accession number?
- Accession number
- DDBJ
We cannot answer necessary days to issue accession number(s) because it depends on the contents of your submission.
If you do not receive any email from DDBJ after 7 working days, please contact us from Contact.Please make sure not to block E-mails from DDBJ.
DDBJ
In case of using DDBJ Nucleotide Sequence Submission System, please confirm whether you have received a mail from DDBJ with “DDBJ: Web submission completed” in its subject or not. This mail is automatically sent to contact person, when DDBJ accepts your sequence data via Nucleotide Sequence Submission System.
- If you have NOT received the mail,
- your submission is not yet finished, so, please complete your submission.
- If you have received the mail,
- please contact us from Contact with contact person E-mail address and Submission ID of your data.
DRA
Login D-way and check the status of your DRA submission.
-
Is there any case to reject submission to DDBJ?
- Submission
- DDBJ
See Acceptable data for DDBJ and Not acceptable sequences.
If you have any question, please contact us from Contact.Reference: Is there any restriction of sequence length to submit to DDBJ?
-
I lost my accession number
- Accession number
- DDBJ
If you have specific ID for your data other than accession number, such as EntryID or any, contact us from contact form with ID and E-mail address of contact person.
In case of uncertain, tell us following items as far as you know, then we will search your data.- Your name
- Your affiliation at the time of submission
- Your current affiliation
- Your mail address at the time of submission
- Your current mail address
- The date, month and/or year, when you submit your data
- Tool that you used to submit your sequence
- Your sequence(s) (if many, just a few representatives)
- Biological feature of your sequence
When we can not find your data, we will ask you to submit your data as new one.
-
How to describe accession numbers on the academic paper?
- Accession number
- DDBJ
In general, see the rule of the journal (i.e. Instructions to Authors), and follow it.
At INSDC, we recommend you to describe accession numbers in the footnote on the title page of your paper as following;
Note: Nucleotide sequence data reported are available in the DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank databases under the accession number(s)—-‘. -
What is the date in LOCUS line?
- format
- search
- DDBJ
It is the date of the last release of the data.
See LOCUS of Explanation of DDBJ flat file format. -
What is "Direct Submission" in TITLE of REFERENCE 1?
- search
- submission
- DDBJ
It indicates that this data is directly submitted from the submitter. The term is the antonym to “journal scan”.
REFERENCE 1 is the information of submitter(s), not general reference.
So, do not describe “Direct Submission” in the title for literature in REFERENCE 2 or after. -
Is there any reference for Feature/Qualifier?
- Submission
- DDBJ
-
When the data submitted with hold date is published, is there any announcement from DDBJ?
- Data
- release
- DDBJ
If you set the hold date for your data, the data will be published according to Principle of “Hold-Until-Published” data release.
After setting to publish the data, the mail with “[DDBJ] Publicized your data” in its subject is sent to contact person.
So, Do not block E-mails from DDBJ.If the information of contact person is old or invalid, we may be unable to acknowledge publication of your data or any other important announcement.
Contact us from this form to send request by selecting the subject, “Change the contact person, belonging, institution, etc..”. -
Tell us conditions to release unpublished data.
- Data release
- DDBJ
-
I would like to know the date when the data was submitted.
- format
- search
- submission
- DDBJ
In general, you can find accept date in JOURNAL line of REFERENCE 1 on DDBJ flat file.
Please note that some old data do not have the description of accept date. -
There are some possibilities as followings.
- In case of the meantime of data distribution:
The data may be on the process of data distribution. If you are unable to retrieve the data longer than a week, please send us an inquiry including the accession number from Contact. - The specified hold date of the
data is in holidays of DDBJ:
We will release the data after holidays of DDBJ. See also DDBJ Calender. - In case of not yet confirmed the accession number is published
on a paper or others:
Please let us know the paper or other media in which the accession number is described. - In case of the data submitted BEFORE January 1, 1998:
The sequence data be still unpublished after hold date.
In case of 3 or 4, we will check and support it.
Please contact us from Contact by selecting the item, “Updating Submitted Data” with accession numbers.References
- In case of the meantime of data distribution:
-
I like to hold my sequence data until publication of related paper, should l specify the hold date?
- Data release
- DDBJ
See “Why is the hold-date required?”. Please specify the date.
Though DDBJ does not restrict the date, we strongly recommend to specify the date within two years.
If not specified, the data will be published, immediately.After data submission, you can change the hold date as needed.
Contact us from this form by selecting “Change the hold-date” in [Subject]. -
How are the data released from DDBJ published at ENA and GenBank?
- Data release
- DDBJ
DDBJ is functioning as one of International Nucleotide Sequence Databases, including ENA/EBI in Europe and GenBank/NCBI in the USA as the two other members.
When DDBJ releases the submitted data, ENA and GenBank will load the data into their own services, respectively. -
How long are the temporal differences of data releases among DDBJ, EMBL-Bank and GenBank?
- Data release
- DDBJ
In general, the data released from EMBL-Bank or GenBank are loaded into DDBJ services and published from DDBJ within their released date.
The data released from DDBJ are loaded into ENA/EBI and GenBank and published from them within a few days.
However, the data release processes at all three databases may be delayed, because of system maintenance, troubles on the network, or any other reasons. So, we can not specify the temporal differences among them. -
The amino acid sequence for CDS feature will be automatically translated from nucleotide sequence according to location and other items, and reflected into /translation qualifier. So, in general, do not enter it.
-
The amino acid sequence in the value of /translation qualifier seems to be incorrect.
- format
- search
- submission
- DDBJ
The rule to translate nucleotide sequence into amino acid sequence is specified in accordance with agreements of International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration.
The codon table using a CDS feature is specified in the value of /transl_table qualifier as a number of The Genetic Codes.There are three points frequently misunderstood.
- You should specify /organelle qualifier to assign correct genetic code for mitochondrion or chloroplast.
- The initiation codon is M, Met, methyonine, not G or V.
See Start codon and N-Formylmethionine - When an amino acid can be specified by two bases (i.e. degeneracy of codons), it will be outputted.
There are some exceptional cases, represented by RNA editing and so on.
-
Which should I use to submit to DDBJ, Nucleotide Sequence Submission System or Mass Submission System?
- Submission
- DDBJ
Nucleotide Sequence Submission System (NSSS) is an interactive application to enter all of items required for your submission on step by step basis.
To use Mass Submission System (MSS), submitters have to make submission files by themselves.
However, since NSSS can not accept all types of sequence data, it may be required to use MSS for your data submission.Use Submission navigation.
See Workflow of the data submission to DDBJ
Based on above information, select either of them as needed. -
How many data can I submit by using Mass Submission System?
- Mass Submission System
- DDBJ
You can use Mass Submission System (MSS) not only for many sequences but also for one long sequence with many features (i.e. complete genome with annotation).
There is no limit of the number of sequences to use MSS and, in some cases, it is required to use of MSS by factors other than the number of sequences.
Use Submission navigation.
See Workflow of the data submission to DDBJ -
How can I check my sequence to exclude vector contamination?
- Sequence data
- DDBJ
See Nucleotide sequences.
You can use VecScreen.
-
How to suspend and resume my submission?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
-
How can I get protein_id?
- Submission
- DDBJ
The protein_id will be automatically assigned at DDBJ during release of your nucleotide sequence with CDS feature.
-
How to entetr two or more features for a sequence?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
At 6. Template, a) select ‘other’ and click [Input annotation] or b) Click [Upload annotation file].
Then, you can describe two or more features for each sequence as follows.In case of a), see 7.Annotation (Annotation when template “other” is selected).
In case of b), see 7. Annotation: Submission by uploading the annotation file.
-
How can I describe DEFINITION?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
Since DEFINITION is constructed by DDBJ according to rules, there is no field to enter it.
-
Can not find input field for some qualifier
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
Click [Select Qualifier], check qualifiers in the dialog as needed and click [Save] button.
Then, you can find input fields for qualifiers on 7.Annotation.Related to this issue, in case of selecting “other” on 6. template, you have to specify some features other than source. So, click [Add feature] and select some feature on the list.
Reference
7.Annotation (when “other” was selected at template) -
How to fix error message: "First codon [***] is not a start codon." / "Final codon [***] is not a stop codon."?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
These errors mean amino acid translation for CDS (protein coding sequence) feature is not appropriate in the 5’ or 3’ end, respectively. When the CDS feature is not complete (i.e. partial) at 5’ and/or 3’ ends, its location is required to include flag for ‘not complete’. According to rules on Description of Location, partial sequences should be appropriately specified with flags for 5’ end not complete, “<”, and/or for 3’ end not complete, “>” on its feature location.
location condition <1..295 [not start with initiation codon] and [stop with termination codon] 1.. >295 [start with initiation codon] and [not stop with termination codon] <1.. >295 [not start with initiation codon] and [not stop with termination codon] For example: partial CDS feature in the range, 1..295
-
How to fix error message: "To use [translation] qualifier, [exception] qualifier is required in the [CDS] feature." ?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
This error message is outputted, because you select /translation for CDS feature by dialog of [Select Qualifier] button.
Generally, since /translation qualifier is automatically created according to items under CDS feature, do not enter any amino acid sequence.
So, you can fix the error by removing /translation qualifier.For your information, /translation qualifier is required only in case describing with /exception qualifier.
Typically, /exception qualifier indicates “RNA editing” is occurred on mRNA. In that case, conceptual amino acid translation of genome sequence is different from protein product of real mRNA molecules.- References
- Description Examples of Sequence Data: B09) RNA editing
- How can I input amino acid sequence (/translation qualifier) for CDS feature?
- How to confirm translated amino acid sequences (i.e. /translation qualifier) for CDS features?
- The amino acid sequence in the value of /translation qualifier seems to be incorrect.
-
How to fix error message: "Invalid value [***] for [transl_table] qualifier."?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
The error is occurred because you do not enter correct genetic code.
See 7.Annotation – Organism name.
To specify genetic code, enter digit in the input field.
The value will be automatically applied for /transl_table qualifier for CDS feature.For your information, in case of a previously reported organism, the genetic code is automatically specified, by describing Scientific name (/organism qualifier) and /organelle qualifier. If your sequence is derived from an organelle other than nuclei, you have to specify /organelle qualifier to set the genetic code for mitochondrion, chloroplast or some, appropriately.
-
browser still waiting for response on the process of data input
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
At first, please save the URL of the page of Nucleotide Sequence Submission System.
Then, clear cache of the browser and reopen the saved URL.
It is likely to resolve the condition.If not resolved, confirm if you use either of browsers Firefox or Chrome that we recommend to use.
If not, change to Firefox or Chrome and reopen the URL.If you still have any problem, please contact us with followings from contact form by selecting the item, “DDBJ : Nucleotide Sequence Submission System (NSSS)”.
- URL
- Number of your sequences
- OS: Windows, MacOSX, or Linux, and its version
- Browser: software and its version
-
How to fix error message: "Value of [ codon_start ] is not 1, but [###..###] is 5' complete type."?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
You may enter incorrect values for Location and/or /codon_start of CDS feature.
If the value of /codon_start is either of “2” or “3”, the location of CDS feature should be 5’ end not complete.See Description of Location and modify the location with flag for “5’ end not complete”, for an example, from “1..300” to “<1..300”.
When the CDS feature is started with an initiation codon, correct /codon_start with “1”. -
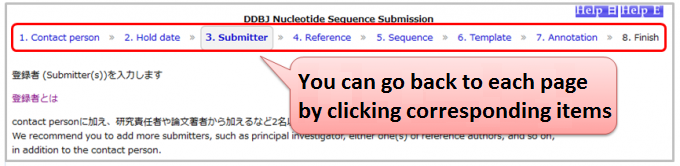
Can I modify descriptions on a previous page?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
You can modify your inputs on any pages before finishing your submission.
You can go back to each page by clicking either of 1.Contact person, 2.Hold date, 3.Submitter, 4.Reference, 5.Sequence, 6.Template or 7.Annotation in progress bar at upside of pages.- ※Caution
- After inputting feature annotation on 7.Annotation, if you do either of followings, feature annotation will be removed.
- modify your sequences on 5.Sequence
- change your template on 6.Template
-
I can not upload my annotation file
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
Confirm following points.
- You have to input the same entry names for both sequences and in annotation file.
- The format of annotation file must be tab delimited text consisting with 5 columns.
- The line feed code of annotation file must be in LF (unix format) or CR-LF (windows format).
- You have to use correct names for feature and qualifier keys.
If you still have any problem, contact us from Contact.
-
How to submit more than one sequence at once?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
On 5.Sequence, input all of your sequences in multi-FASTA format. We will assign consequent accession numbers for your sequences.
Moving to 7.Annotation, you can enter feature annotation for each sequence at once.
Caution- All of following items must be unified for all sequences. You can not specify thenm for each sequence.
- Contact person
- Hold date
- Submitter
- Reference
- You can select only one template on 6.Template for all sequences. You can not select a template for each sequence.
-
How to confirm translated amino acid sequences (i.e. /translation qualifier) for CDS features?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
You can confirm amino acid sequences for CDS features as follows.
-
Download UME_win.zip (for Windows) or UME_mac.zip (for MacOSX) from Mass Submission System.
-
Download both annotation and sequence files at 8. Finish on DDBJ Nucleotide Sequence Submission System.
-
Run UME and load both annotation and sequence files. Then click [Execute] of transChecker.
The function to confirm amino acid sequences will be applied on DDBJ Nucleotide Sequence Submission System.
-
How to fix error message: "MGA:No entry name is found other than [ COMMON ], without feature [ DATATYPE/type=MGA ]."?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
Though you have not yet enter either /organism or /mol_type on annotation table, you click [Confirm] button.
You must fill mandatory items of annotation (feature, location, qualifier) before clicking [Confirm] button.On 7.Annotation, click [Select Qualifier] button beside ‘source’, and select qualifiers as needed. Then, click [Edit] button beside entry name and input /organism and others. Note that it is required to input at least one feature other than source.
See also 7.Annotation – Organism name. -
How to fix error message: "Stop codon ‘*’ is found in the range."?
- Nucleotide Sequence Submission System
- DDBJ
In general, see How to describe CDS feature, when termination codon is found in the range.
You can also see Protein Coding Sequence; CDS feature to describe CDS feature.
Following items are case study for the error.-
Did you correctly specify /codon_start qualifier to indicate reading frame of the CDS feature?
Select 1, 2 or 3, appropriately.- References:
- Offset of the frame at translation initiation by codon_start
- How to fix error message: “First codon [***] is not a start codon.” / “Final codon [***] is not a stop codon.”? How to fix error message: “Value of [ codon_start ] is not 1, but [
-
Have you specify correct genetic code for /transl_table qualifier?
See followings and specify genetic code, appropriately. -
Are there really some stop codons in the range of CDS feature because of frame shift, nonsense mutation, or some other reason?
-
In case of pseudogene
Click [Select Qualifier] button beside CDS and add /pseudogene qualifier. Then, you can specify /pseudogene qualifier with its controlled vocabularies.
See also b) considered pseudogene in detail. -
In cases of unsure whether it is pseudogene or not, the reason of stop codon is uncertain, or on the process of diversity increasing related to acquired immunity, describe misc_feature, not CDS feature.
See a) Putative nonsense mutation, frameshift caused by uncertain reason, or on the process of diversity increasing related to acquired immunity for IgG etc. in detail.
-
-
In other cases.
There are some possibilities to output this error because of ribosomal slippage, RNA editing, exceptional amino acid usage, transpon insertion and so on.
-
What is secondary accession number?
- Accession number
- DDBJ
INSD; International Nucleotide Sequence Database are composed of DDBJ, ENA and NCBI, and collect experimentally determined nucleotide sequence data.
A unique accession number issued by INSD for each submitted sequence data is defined as the INSD accession number.
On DDBJ flat file, the accession number is described in ACCESSION line.If multiple entries are united to an entry, or if an entry is extensively modified after the submission, the responsible data banks may assign a new accession number to it. In these cases, the new accession number is called the primary accession number, and the old accession number(s) is/are called the secondary accession number(s).
In the flat file, the primary accession number is indicated first, then the secondary accession number(s) follows.
Example
ACCESSION AB999999 AB888888 AB777777
AB999999 – primary accession number
AB888888 AB777777 – secondary accession numberYou can find the same updated entry with both the primary and the secondary accession numbers, in general.
However, if the old entry with secondary accession number has previously been open to the public, the old one is not removed. So, you can find the old record by getentry.References
-
What is the difference between env_broad_scale, env_local_scale and env_medium?
- Sample
- attributes
- BioSample
These three sample attributes describe environmental systems have influences on living organisms.
env_broad_scale
Add terms that identify the major environment type(s) where your sample was collected. Recommend subclasses of biome [ENVO:00000428]. Multiple terms can be separated by one or more pipes e.g. mangrove biome [ENVO:01000181]|estuarine biome [ENVO:01000020]env_local_scale
Add terms that identify environmental entities having causal influences upon the entity at time of sampling, multiple terms can be separated by pipes, e.g.: shoreline [ENVO:00000486]|intertidal zone [ENVO:00000316]env_medium
Add terms that identify the material displaced by the entity at time of sampling. Recommend subclasses of environmental material [ENVO:00010483]. Multiple terms can be separated by pipes e.g.: estuarine water [ENVO:01000301]|estuarine mud [ENVO:00002160] -
What should be provided when information is unavailable?
- Metadata
- BioSample
Please see the Missing value reporting.
-
How are linked BioProject/BioSample/experimental data released?
- Data release
- BioProject
- BioSample
- DRA
- GEA
- MetaboBank
Linked BioProject, BioSample, DDBJ, DRA, GEA and MetaboBank data are released as follows.
- Release of the BioProject and BioSample records DO NOT trigger release of the other linked data.
- Release of the BioSample records trigger release of the referencing BioSample in derived_from attributes.
- Release of the DDBJ, DRA, GEA and MetaboBank data DO trigger release of the linked BioProject and BioSample records.
- Release of DDBJ triggers release of DRA Run(s) linked from DBLINK(s).
- Release of GEA triggers release of linked DRA Run(s).
- Release of the DRA data DO NOT trigger release of the DDBJ records.
All metadata and sequencing data in a DRA submission are released at once.
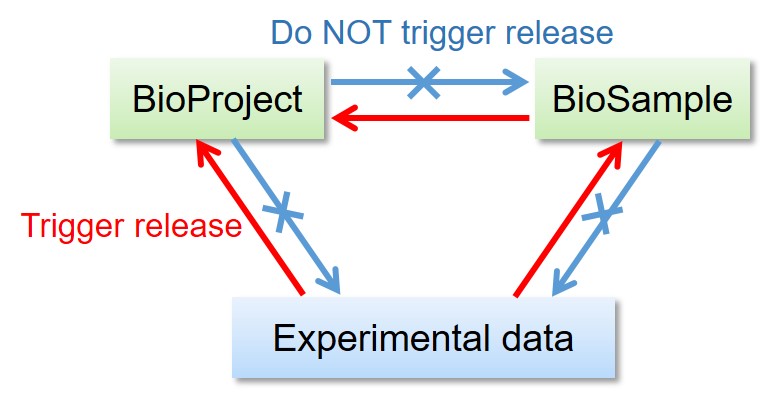
Release of linked BioProject/BioSample/experimental data 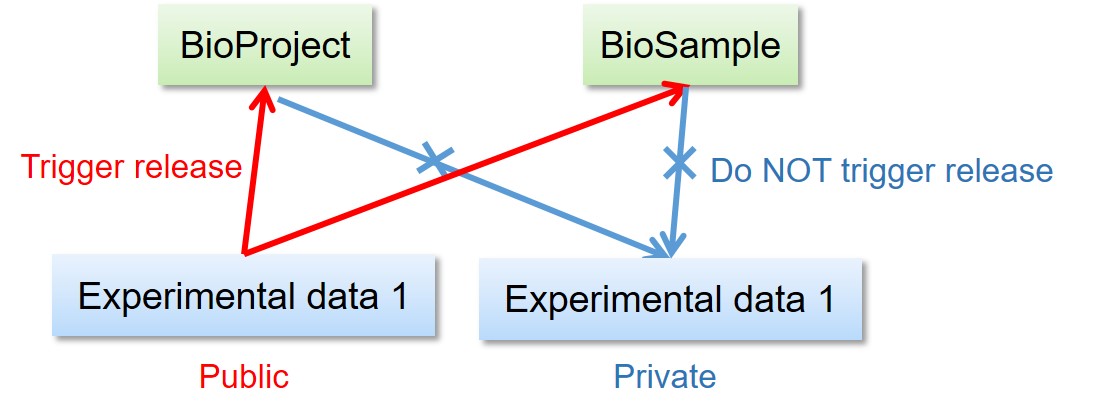
Release of the other data linked to BioProject/BioSample 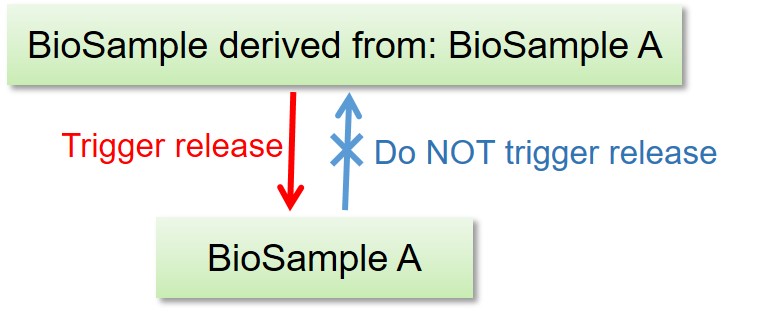
Release of derived BioSample -
How are my data files processed?
- Sequencing data
- DRA
Uploaded data files are processed per Run. All files under a Run are merged into single binary SRA file by using SRA toolkit. During this conversion, length and format of all reads are checked.
Read names are editted and identifiers (DRR accession number + serial number) are automatically inserted (example: DRR000001).
Original read names should be unique in a Run.
A DRR accession number is used as a filename. If the fastq is selected for the filetype, read names are replaced with the DRR accession number + serial number. (example: DRR030615).When “PAIRED” is selected in Experiment, paired reads are grouped in a Run.
DRA generates fastq from SRA files by using SRA toolkit and provide sequencing data in both file formats.
More than two fastq files are provided for paired reads. Paired reads are divided into a file with “_1” (example, DRR000001_1.fastq.bz2) and “_2” (example, DRR000001_2.fastq.bz2). Reads without pair are provided in a file without “_1” nor “_2” (example, DRR000001.fastq.bz2).
-
Regarding the E value displayed in the BLAST analysis results: How is this value calculated?
- Analysis
- BLAST
The E value is computed using the following formula, in which l denotes the length of the query string, n denotes the number of strings stored in the database, and S is a score that measures the homology between nucleic acids or between amino acids. Note that k and m are positive constants.
E=k*l*n*exp^(-mS)
If the BLAST output results computed using this formula are displayed in the form 1E-X, this means that the quantity has the value 10-X. -
BLAST search results are displayed in descending order of homology score.
There is no way to assign priorities to strings with identical scores, so there is no particular regularity to the order in which such strings are displayed. -
The number of search results shown is too small! (I receive the message “No hit found.”)
- Analysis
- BLAST
If the number of search results shown is fewer than the number specified for the options “Number of Search Results to Display” and “Number of Alignments to Display,” you may increase the number of displayed results by increasing the value of the “Expectation value” under the “Advanced settings” field.
In such a case, try setting the expectation value to an extremely large number such as 10,000.
Note that, if the string is too short (a sequence length of 10 or so), BLAST will frequently be unable to find matches. -
The sequence that you entered was filtered by the BLAST program.
The filtering has the effect of replacing regions of your input sequence of low structural complexity with “N” (or “X” for amino-acid sequences). For details on filtering, see the section “FILTER” in the BLAST HELP. To disable filtering, select the OFF radio button in the “FILTER” option in the lower portion of the Settings screen.
Note with caution that setting this option to “OFF” may result in search times that are longer than normal. -
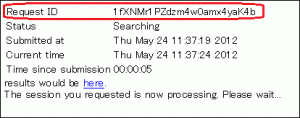
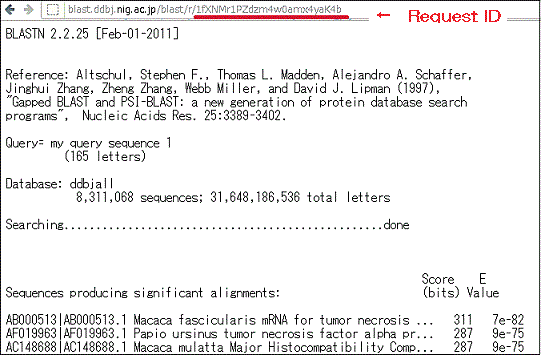
Is it possible to view search results at a later time?
- Analysis
- BLAST
- Search results may be accessed via the following URL, which contains a Request ID field.
- http://blast.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/blast/r/Request ID
- Request ID
- Note that the Request ID will be displayed in the window that appears after transmitting the input. Make sure to note down this.
- Reading period
- Search results may be viewed up to 7 days after the execution of the search.
-
Please see the DDBJ home page References.
-
The format differs from journal to journal; please ask the publisher.
In your publications, please cite the original papers for the appropriate tools and state that you used DDBJ software for searching and analyzing gene sequence data.Please see the DDBJ home page References about the original papers and other related papers on the DDBJ search and analysis software.
-
Does DDBJ offer data search and analysis services?
- Search
- Analysis
- DDBJ
There are two ways of searching and analyzing data, as discussed below. Please select the option that is appropriate for your needs.
- Conducting searches and analyses using a network server such as an
FTP or web server.
You may access these networking tools via Search / Analysis. - Conducting searches and analyses by logging in to the supercomputer
system at the National Institute of Genetics (NIG).
(This requires a supercomputer user ID. You will need to sign up for a new user account on the NIG supercomputer system.)
-
I did not obtain the search results that I was expecting. Did I make a mistake in conducting my search?
- Search
- Analysis
- ARSA
- BLAST
- getentry
The DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank data banks share the sequences stored within each data bank, and in principle all three data banks should contain the same data. However, due to time delays in the inter-data-bank sharing of data released by individual data banks, as well as delays between the time at which data are entered into a data bank and the time at which the data are reflected in the corresponding search service, searches conducted using different services at the similar time on the same day may yield slightly different results. If you do not obtain the search results that you were expecting, time delays of this sort are the most likely culprit; however, for cases requiring a more detailed investigation, please contact the DDBJ via the “Other” section of the contact portal. In this case, make sure to specify the following information:
- The name of the search program and/or the URL that you used to conduct the search.
- The search conditions that you used.
- The date and time at which you conducted the search.
- Accession number of the entry that should have been found.
- URL of the search results.
- Any other relevant information.
Also, please see the sections of this document corresponding to the following questions.
-
Regarding the phrase “after a scheduled DDBJ release”: When, specifically, does this phrase describe?
- DDBJ
- release
- DDBJ
“Newly arrived DDBJ data (new data that have arrived after a scheduled DDBJ release)” are data made publicly available on the next day of the deadline or after for the most recent DDBJ release. The deadlines for the most recent releases are listed in the text of the release notes. For example, if the most recent release were Release 67, then the deadline would be 8/25/2006, as stated below; thus, in this case, “newly arrived DDBJ data” would be data made publicly available after 8/26/2006.
The present release contains the newest data prepared by the DNA Data Bank ofJapan (DDBJ), GenBank (*), and European Molecular Biology Laboratory/EuropeanBioinformatics Institute (EMBL/EBI) as of August 25, 2006. (This statement comes from the release notes for Rel. 67; the remainder of that discussion is omitted here.)
-
The services that exist for communicating information about DDBJ are as follows.
Choose whichever resource is most appropriate for your purposes. -
While no limitations are placed on information citations from the DDBJ website, DDBJ is not responsible for websites that cite information from DDBJ or how the cited information is displayed.
When citing information from this website, please clearly indicate that the information has been taken from the DDBJ website.If possible, please let us know the following information from Contact
- The website on which the information will be cited (or where image(s) will be reproduced)https://forms.gle/ZXteuEPM4SSm5HUt8
- The URL or the image(s) that will be cited
-
Please distribute clones.
- Use
- DDBJ
The DDBJ is a database center of nucleotide sequences, so it does not distribute any clones.
Please contact the submitter of the clone sequence directly. -
How can I turn the "Validate data files" button active?
- Sequencing data
- DRA
When all sequencing data files listed in the Run metadata are uploaded to the DRA server, the “Validate data files” button becomes clickable and users are able to start the validation process.If the button remains inactive after submitting metadata (“Metadata Submitted”), check the following points.
- Have all data files listed in the Run metadata been uploaded?
- Doesn’t data files contain spaces?
- Aren’t uploaded files contained in sub-directories?
-
How do I update my BioProject?
- Update
- BioProject
Contact the BioProject team to request updates and withdrawals.
-
How do I update my BioSample?
- Update
- BioSample
It is necessary for submitters to contact the BioSample team to request updates and withdrawals as necessary. You can confirm updated samples by downloding the attribute tsv (example, SSUB000001.txt) in the ATTRIBUTES of the D-way BiSample submission page.
-
Is there any restriction of sequence length to submit to DDBJ?
- Submission
- DDBJ
- Upper limit
- If the sequence is really observed, there is no upper limitation of the sequence length to submit to DDBJ.
However, we can not accept any operationally joined sequence, for example, joining chromosomes. We accept each chromosome sequence, respectively.
For whole genome scale sequences, submit by using Mass Submission System (MSS) instead of Nucleotide Sequence Submission System (NSSS).
See Workflow of the data submission to DDBJ - Lower limit
- Since June 2021, when the sequence is less than 100 bp in its length, we will refuse the sequence data submission.
- References
- Is there any case to reject submission to DDBJ?
- Acceptable data for DDBJ
- Not acceptable sequences
-
Where to submit variant data, such as Single Nucleotide Variants (SNVs), Copy Number Variants (CNVs) and structural variants?
- Submission
- TogoVar
TogoVar-repository accepts human variation data.
TogoVar-repository is a public repository for submissions of human genetic variants, allele and genotype frequencies. TogoVar-repository accepts submissions of human genetic variations in two categories and issues accession numbers with distinct prefixes: short variants (≤50 bp) and large structural variants (>50 bp).- Short variants: variants ≤50 bp including single nucleotide variations, microsatellites, and small-scale insertions and deletions. Variation data exchange with the NCBI dbSNP is planned.
- Large structural variants: variants >50 bp including insertions, deletions, duplications, inversions, mobile elements, translocations, and complex variants. Variation data exchange with the NCBI dbVar is planned.
TogoVar-repository and dbSNP/dbVar only accept variations of human. European Variation Archive accepts variations of both human and non-human organisms.
-
How do I get a FASTA format of WGS, TSA, or TLS entries?
- Search
- getentry
To get a FASTA format of WGS, TSA, or TLS entries, please use getentry, specifying the following values.
- ID : Specify the Accession Number.
- Output format : Select “total nt seq FASTA” for the result.
- Result : Select one from the following filetype for the output.
- html
- text
- compress (gz)
- Limit : Set an upper limit number of the result.When you specify the Limit “0”, there is no upper limit of the data acquisition. For more information about each value, please see getenry HELP.
-
In the JGA submission, fields including the Subject ID and Gender are required.
Specifically, that the main variable (e.g., heart disease) and co-variates (e.g., age, weight) used in the analysis are submitted to JGA so that other people can reproduce the information in your publication.
The goal is to include the data that would be required for another researcher to be able to reproduce the published analysis. -
Do DDBJ JGA/NCBI dbGaP/EBI EGA exchange data?
- Data exchange
- JGA
DDBJ JGA / NCBI dbGaP / EBI EGA do not exchange data.
-
Sequence format acceptable for submission (FASTA, multi-FASTA)
- Sequence data
- DDBJ
For the DDBJ nucleotide sequence submission system (NSSS), you must input nucleotide sequence(s) in FASTA format (for 1 sequence only) or in multi-FASTA format (for 2 or more sequences).
Related page: Format of the nucleotide sequences that you can paste or uploadYou must insert the end flag (//) at the end of each sequence when you use MSS for your submission. Please see “How to Make Sequence File”.
See also Wikipedia, FASTA format
-
Please see our policies.
-
Please see About Acknowledgements.
-
Application form for Data Update Requests is not displayed
- Contact form
- DDBJ
Subject : Select from the following items.
- Our paper was publishied
- Our paper was accepted
- Change the hold-date
- Change discription about the contact person
To : Data updates / Corrections (click the service name to send an e-mail)
Body :(* Required)- [For all subjects]
- Applicant Name*
- Applicant Email address*
- Contact person Name(When you are not contact person, please input this item.)
- Contact person Email address(When you are not contact person, please input this item.)
- Accession Numbers*
- [Our paper was publishied]
- Paper Title *
- Paper All authors *
- Paper Journal *
- Paper Volume
- Paper Issue
- Paper Start page - End page
- Paper Year
- Paper URL
- Paper PubMed ID
- Paper DOI
- [Our paper was accepted]
- Paper Title *
- Paper All authors *
- PaperJournal *
- Paper Volume
- Paper Issue
- Paper Start page - End page
- Paper Year
- Paper URL
- Paper PubMed ID
- Paper DOI
- When will you release the data?(Select from the following items.)*
- Release immediately
- Specify the hold-date → Please specify the hold-date
- [Change the hold-date]
- New hold-date(Select from the following items.)*
- Release immediately
- Specify the hold-date → Please specify the hold-date
- [Change discription about the contact person]
- Name ( Current )
- Name ( Update )
- Email address( Current )
- Email address( Update )
- Institution ( Current )
- Institution ( Update )
- Address ( Current )
- Address ( Update )
- [For all subjects]
- Message
-
Contact form is not displayed
- Contact form
- DDBJ
* Required
Name*
E-mail address*
Affiliation*
Title*
Accession number/Submission ID
DDBJ account
Request ID
User ID
Contacts*Contacts(click the service name to send an e-mail)
- DDBJ Nucleotide Sequence Submission System (NSSS)
- Data updates / Corrections
- Mass Submission System (MSS)
- BioProject/BioSample/Sequence Read Archive (DRA)
- DDBJ Account
- Japanese Genotype-phenotype Archive (JGA)
- Search / Analysis
- DDBJ Read Anotation Pipeline
- Training course
- NIG SuperComputer system
- Other
-
Mutual data exchange between NCBI GEO and ArrayExpress is not realized so GEA data are not shared with GEO. ArrayExpress had been imported GEO data, however, this import was suspended.
BioProject and BioSample registered during GEA submission are exchanged with NCBI/EBI in the framework of INSDC.
-
Could you show me the registration flow for MSS?
- Mass Submission System
- DDBJ
Please visit the Registration process in MSS for detail.
-
Can only sequence file be accepted for an MSS submission?
- Mass Submission System
- DDBJ
No. Both annotation and sequence files are necessary for an MSS submission.
Please visit the following sites for detailed instructions to prepare submission files. -
How to provide my private data to journal reviewers?
- System
- Data release
- DDBJ
- DRA
- GEA
- MetaboBank
- JGA
- GEA: By using the reviewer access, you can provide metadata, microarray data and NGS processed data to reviewers.
- MetaboBank: If you want to provide a reviewer access, request through Application Form for MetaboBank Update.
- DRA: You may send a metadata summary list attached to the accession number notification e-mail. For sequencing data, download archived fastq files and provide them to reviewers through access-controlled file sharing services or servers.
- DDBJ: See “How can we show our submitted sequence in private status to reviewers?”.
- JGA: We can not offer the reviewer access service due to the policy.
Reviewer access services are not available in DRA, DDBJ and JGA.
For open-access databases (GEA/MetaboBank/DRA/DDBJ), if you make your data public, all users including reviewers can access the data.
-
I can not transfer files by using sftp
- System
- DDBJ
- DRA
- GEA
- MetaboBank
- JGA
Confirm the following points.
- Authentification is by using SSH key not by password.
- A private key is pair of a public key registered in a DDBJ account. Manual
- Make sure to specify a private key for authentification and not a private key for dataset encryption/decryption. Manual
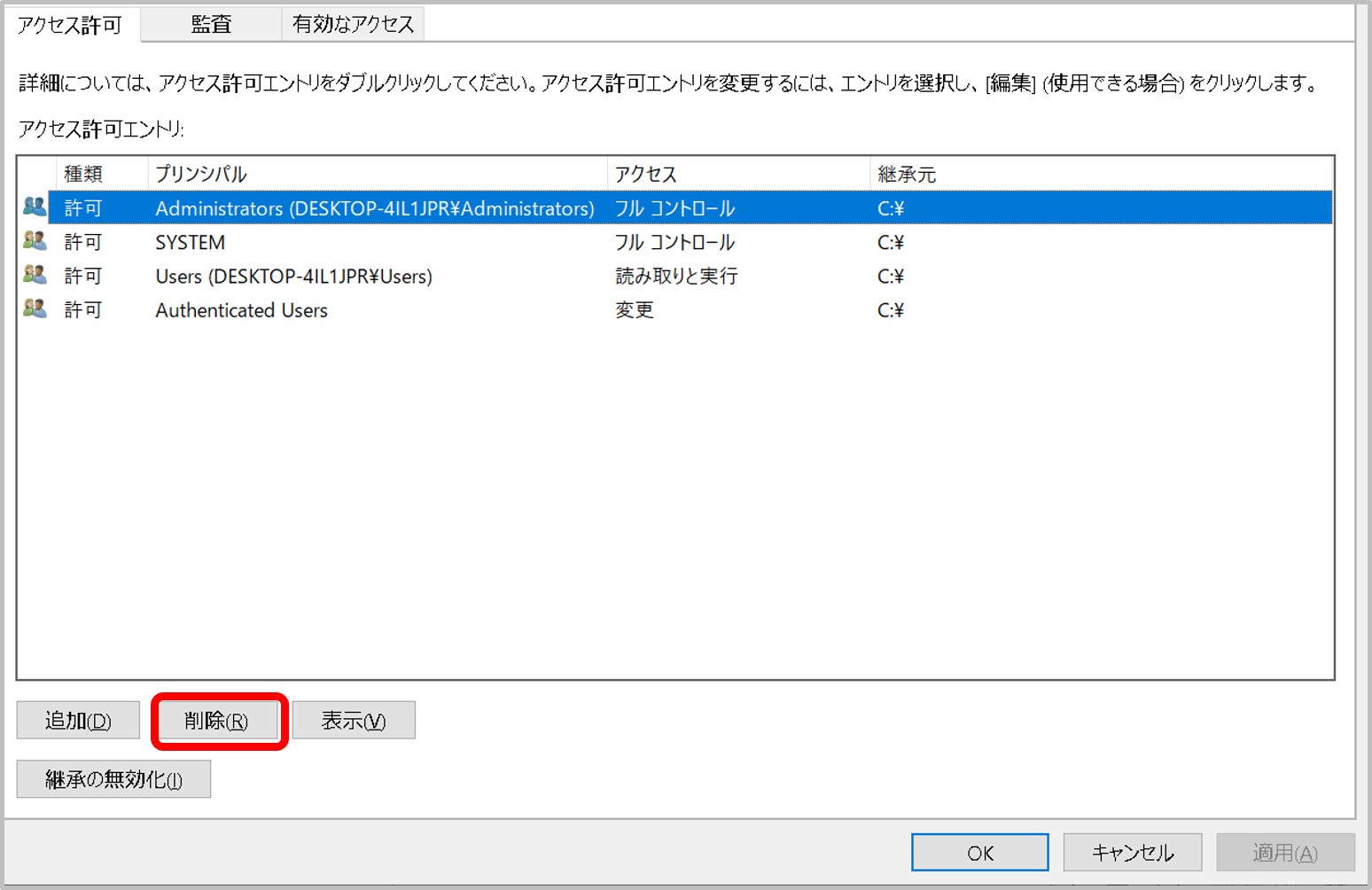
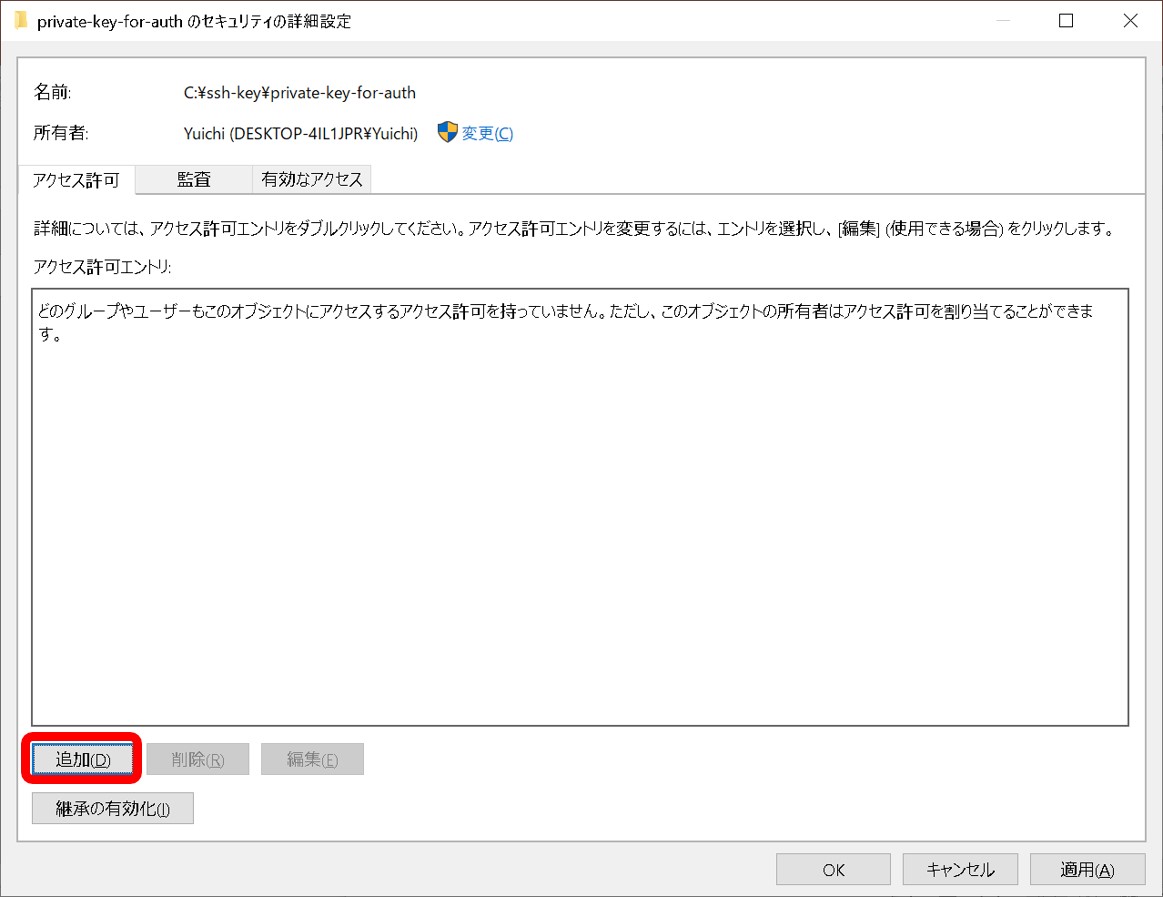
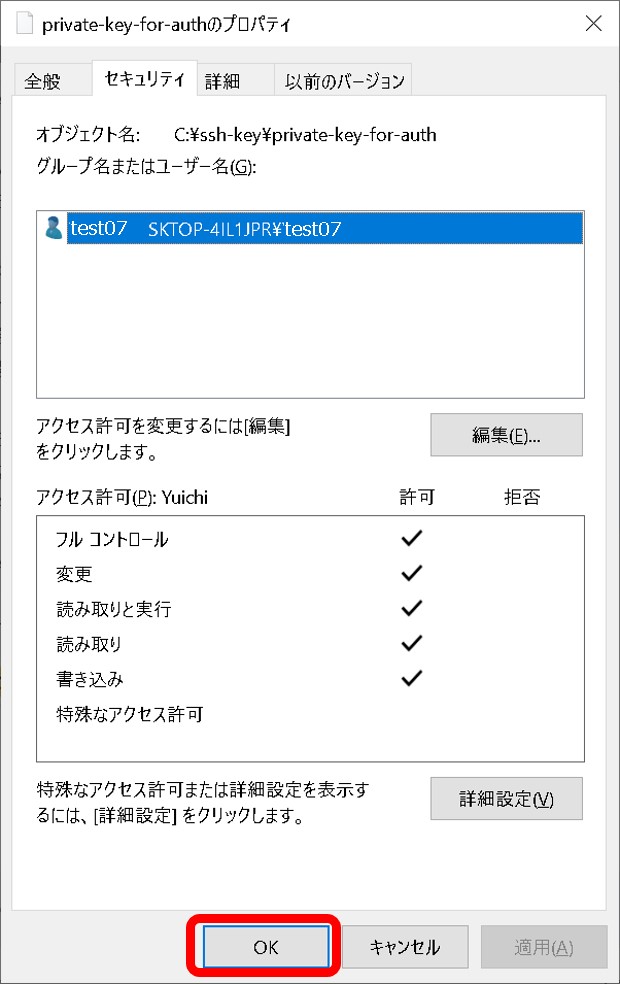
- A private key file has read permission.
- A private key file permission is set as others cannot access. For example, rw——-.
- A passphrase for private key is correctly entered.
- The ssh connection with the port number 22 (DRA/GEA/DDBJ/MetaboBank) or 443 (JGA) is allowed in your network (Please ask your network administrator)
When transferring data files by using a private key generated in the other operating system, please check format of a private key. Convert private key
- In Unix/Mac OS X: Convert a key in the Windows PuTTY file format into the OpenSSH.
- In Windows WinSCP: Convert a key in the Unix/Mac OS X OpenSSH file format into the Windows PuTTY format.
When these are correct, because we do not support technical details regarding use of third-party softwares, please refer to websites of softwares or confirm your system administrators whether ssh, port 22 (DRA/GEA/DDBJ/MetaboBank) and 443 (JGA), is allowed or not.
Accounts newly created on the DDBJ Account system are immediately available for use via sftp. However, it may take about 15 minutes before they can be used in D-way/JGA. Please note this in advance.
Check if communication is allowed in the user environment
As requested, the DDBJ Center will investigate access logs to ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp. If there is no record in the access logs, it is possible that communication is not allowed in the user’s environment.
On April 10, 2025, the IP address of ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp was changed from 133.39.224.111 to 133.39.233.40. Due to this change, communication that was previously allowed in the user environment may now be blocked. Please ask your network administrator to confirm whether communication to 133.39.233.40 on port 22 is allowed.JGA/AGD data transfer server is jga-gw.ddbj.nig.ac.jp 133.39.233.39
Check if the user home directory has been created
If you see the following error message, it is possible that the user home directory has not been created on
ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jpfor DDBJ accounts newly created after April 10, 2025.
The DDBJ Center will create the user home directory on your behalf, so please contact us with your account name.sftp -i id_rsa test07@ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp Enter passphrase for key id_rsa': client_loop: send disconnect: Connection resetConnection closedChecking key pair match
Check by command
You can display the corresponding public key for a private key (e.g., id_rsa) by running the following command:
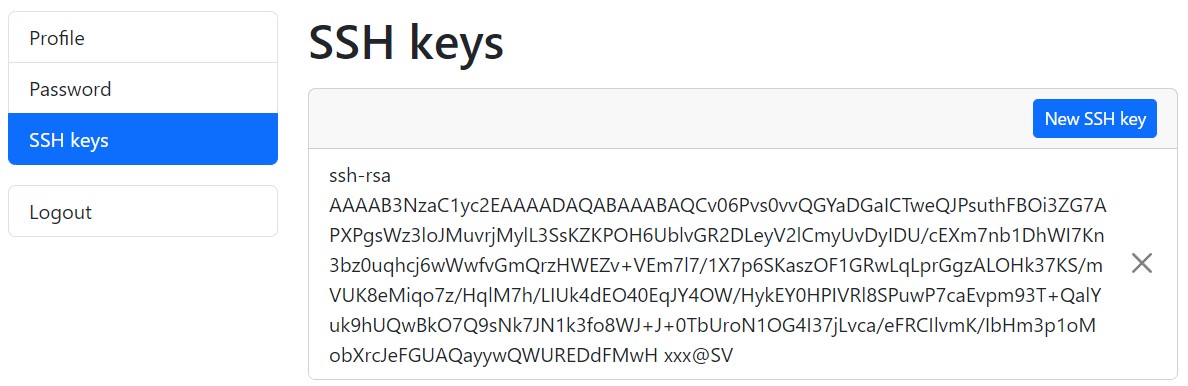
ssh-keygen -y -f id_rsaLog in to your DDBJ account, and display the public keys registered under “SSH keys”.
Compare the contents of both keys. If they match, the keys form a valid pair. If they do not match, the keys are not a pair. In that case, generate a new key pair, specify the private key for SFTP, and add the corresponding OpenSSH-format public key to your DDBJ account. You can register multiple public keys in your DDBJ account.
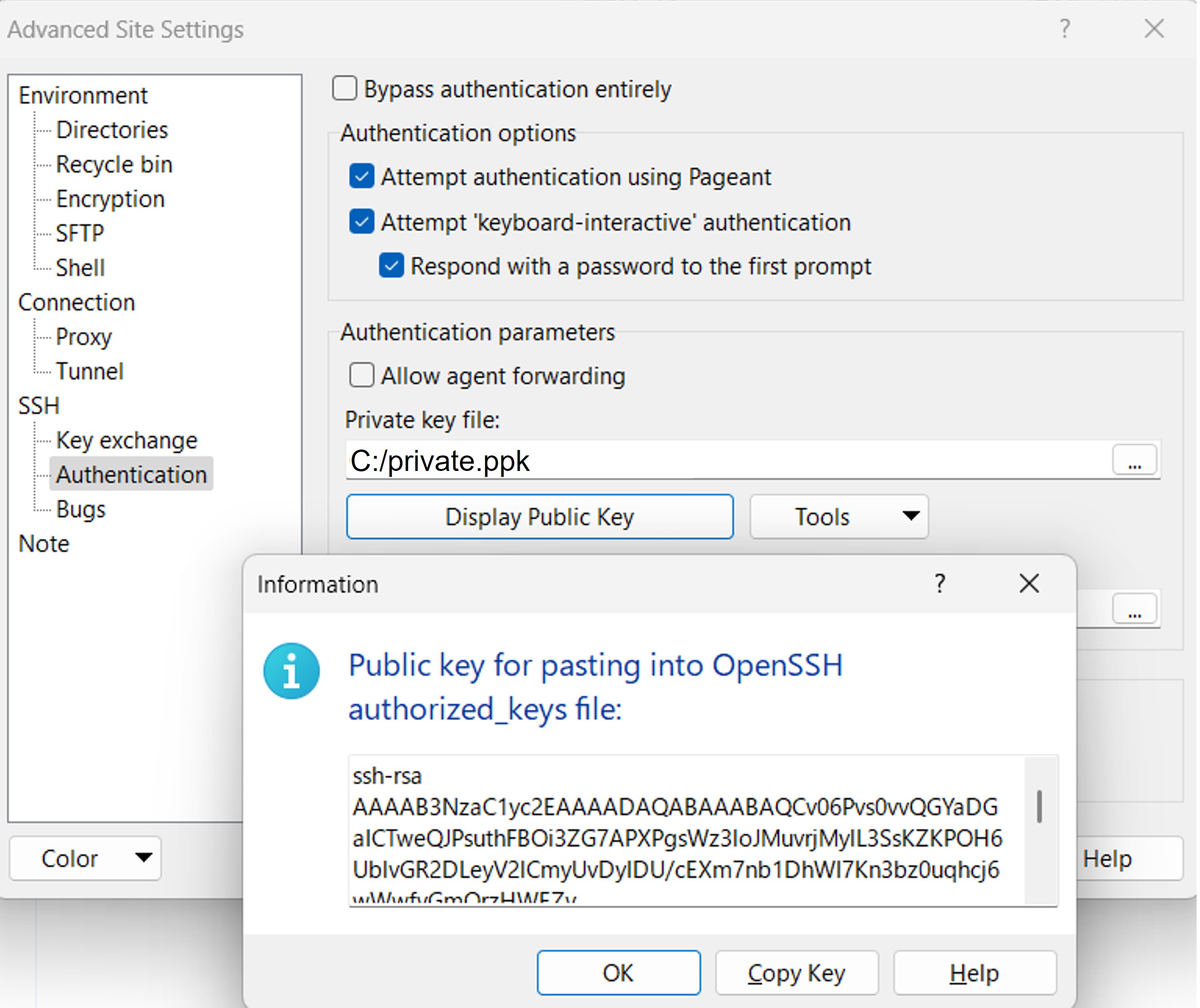
Check by WinSCP
WinSCP displays the public key that corresponds to a private key. You can also check the registered public key in your DDBJ account. By comparing the two keys, you can check whether the private and public keys are a pair.
In WinSCP, go to Advanced Site Settings > SSH > Authentication, and click Display Public Key. This will display the public key that pairs with the private key specified in the Private key file field.
Log in to your DDBJ account, and display the public key(s) registered under SSH keys.
Compare both keys. If they match, the keys form a valid pair. If they do not match, they are not a valid pair. In that case, generate a new key pair, specify the new private key in WinSCP, and add the corresponding OpenSSH-format public key to your DDBJ account. You can register multiple public keys to your DDBJ account.
client_loop: send disconnect: Broken pipe
client_loop: send disconnect: Broken pipeIf the above error appears when using sftp, please take the same measures as for “ssh connection is disconnected”.
ssh connection is disconnected
Please specify the following options with the sftp command.
sftp -o ServerAliveInterval=60 -o TCPKeepAlive=yes -i id_rsa test07@ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jpBy adding the configuration to the
.ssh/configfile in your home directory, you can avoid having to specify the above options with each command.Host ddbj-ftp ServerAliveInterval 60 TCPKeepAlive yes HostName ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp User test07 IdentityFile ~/id_rsaAfter adding the configuration, close the terminal once and reopen it before running the sftp command again.
With the above config settings, you can access sftp using a shortened command as shown below.sftp ddbj-ftpREMOTE HOST IDENTIFICATION HAS CHANGED
The BioProject/BioSample/DRA/GEA systems have been migrated to new supercomputer at 10th April 2025.
Due to this migration, access to ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp may be blocked by the remote host key identification warning.@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ @ WARNING: REMOTE HOST IDENTIFICATION HAS CHANGED! @ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ IT IS POSSIBLE THAT SOMEONE IS DOING SOMETHING NASTY! Someone could be eavesdropping on you right now (man-in-the-middle attack)! It is also possible that a host key has just been changed. The fingerprint for the ECDSA key sent by the remote host is SHA256:LAPCiua8RAlPIZwE4MKWX7YHMY//rtyjfnUYBj/cnfk. Please contact your system administrator. Add correct host key in /Users/test07/.ssh/known_hosts to get rid of this message. Offending ECDSA key in /Users/test07/.ssh/known_hosts:2 Host key for ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp has changed and you have requested strict checking. Host key verification failed. Connection closedDelete a line where “ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp” or the IP address “133.39.224.111” are recorded from the known_hosts file under your home directory (for example, test07).
/home/test07/.ssh/known_hostsYou may know the line number to be deleted from the warning message (example below is 2).
Offending ECDSA key in /Users/test07/.ssh/known_hosts:2After deleting the line of the known_hosts file, access to the server.
Because the access is regarded as a first time access, you are asked whether record the server key or not. Please select “yes” and access the server.UNPROTECTED PRIVATE KEY FILE WARNING
If the private key access permission is too open, following error may be shown.
@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ @ WARNING: UNPROTECTED PRIVATE KEY FILE! @ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ Permissions for './private-key-for-auth' are too open. It is required that your private key files are NOT accessible by others. This private key will be ignored. Load key "./private-key-for-auth": bad permissions test07@ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp: Permission denied (publickey,gssapi-keyex,gssapi-with-mic). lost connectionRight-click the private key file and select the property.
Select detailed setting of the security tab.
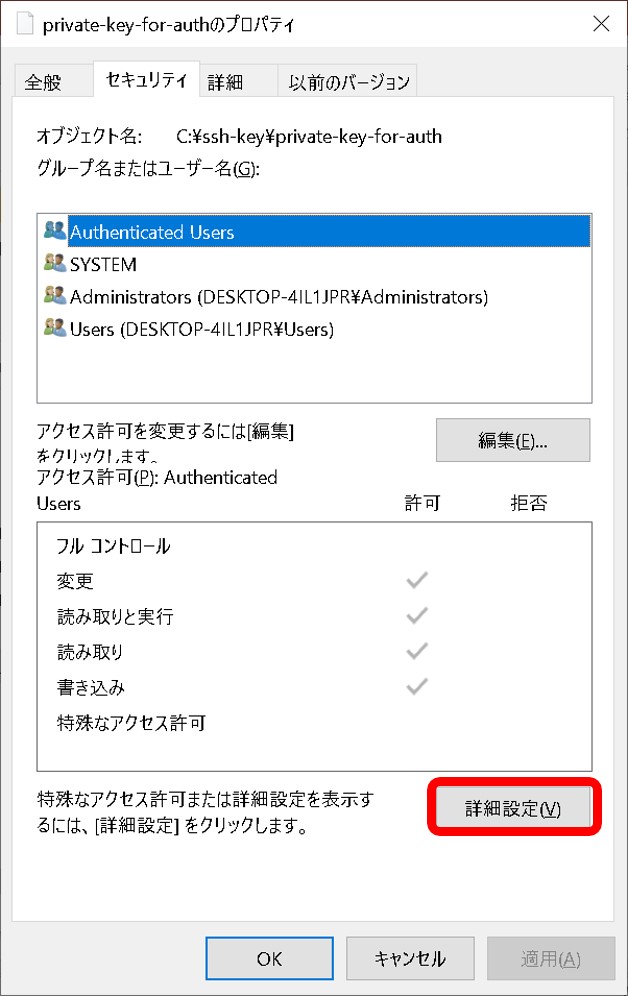
Disable access permission entry inheritance to enable permission deletion.
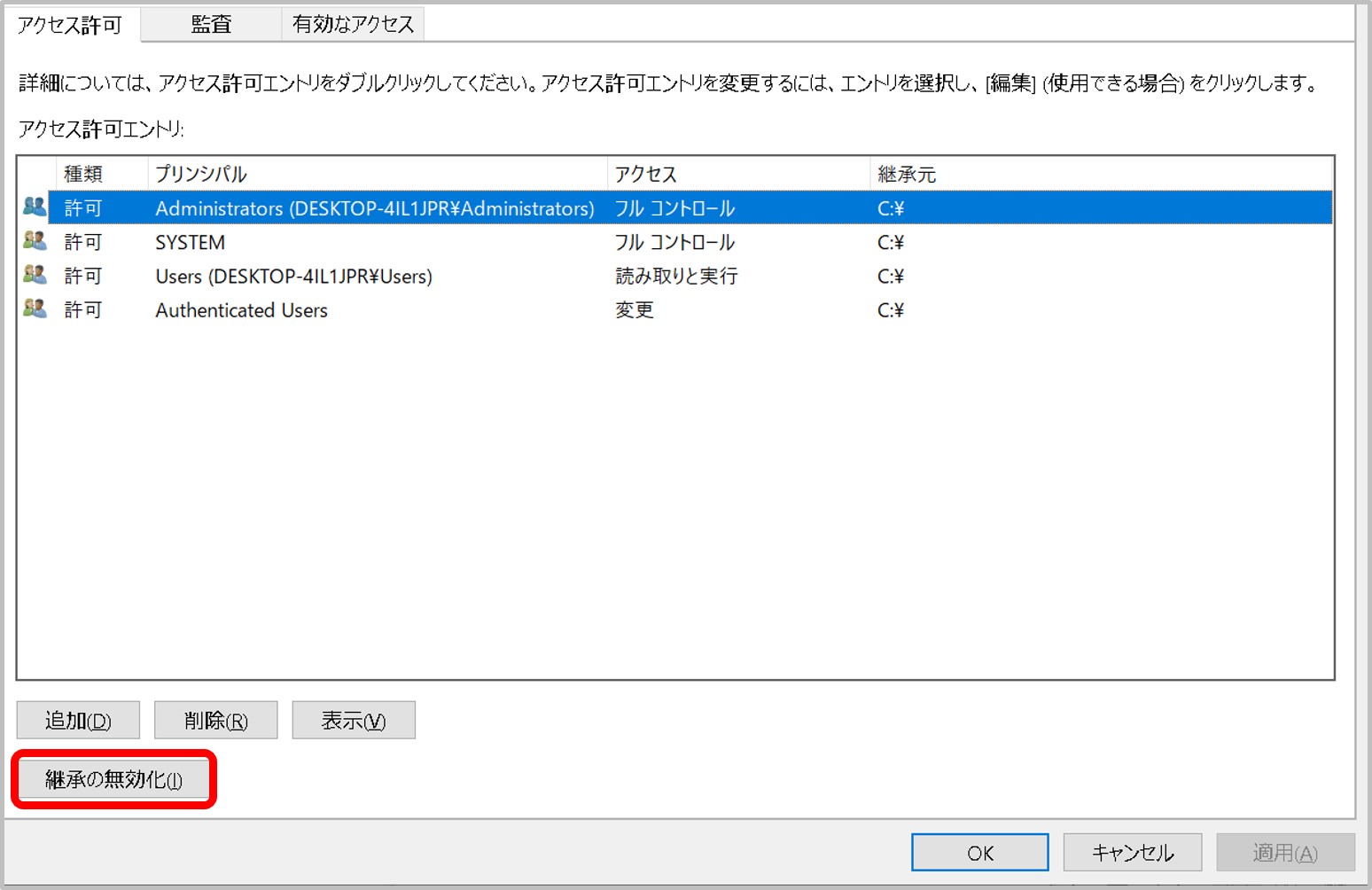
Convert explicit access permission.
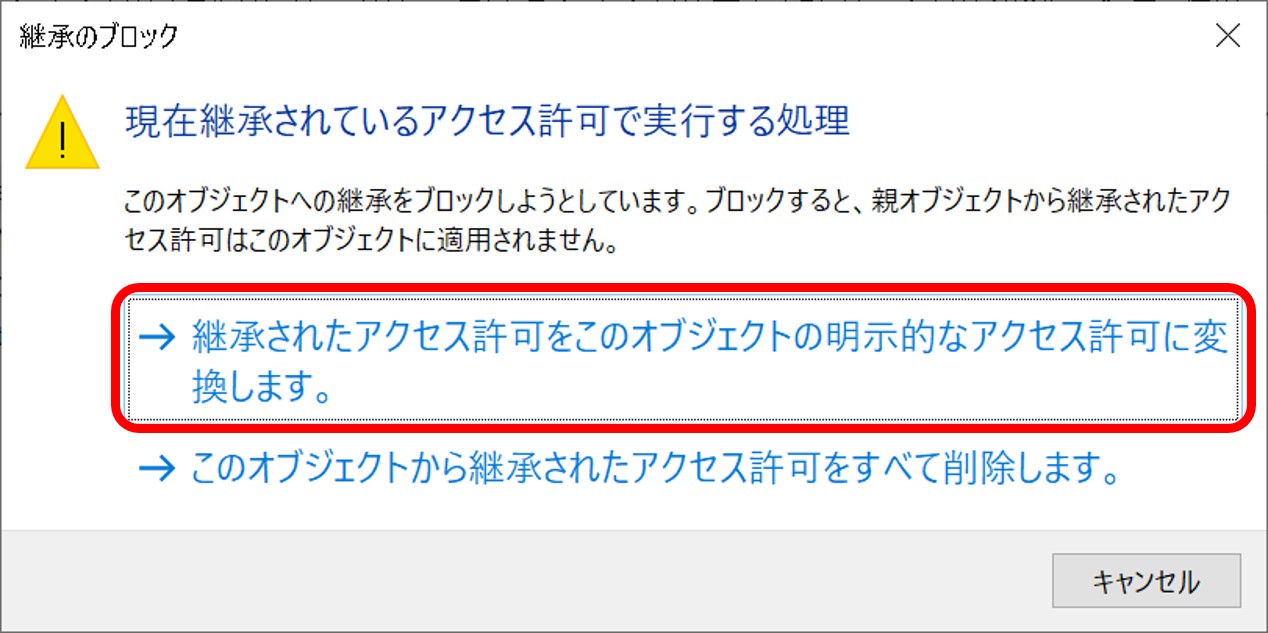
Add a Windows user (example, test07).
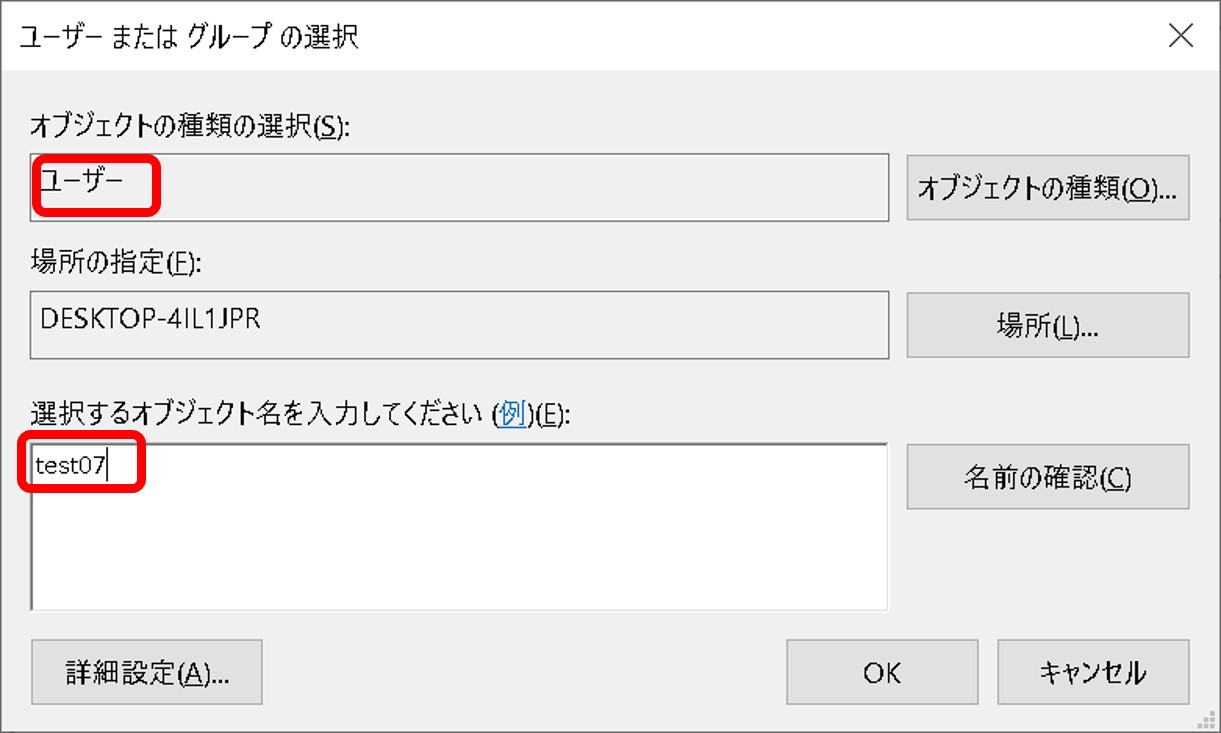
Allow full control to the Windows user.
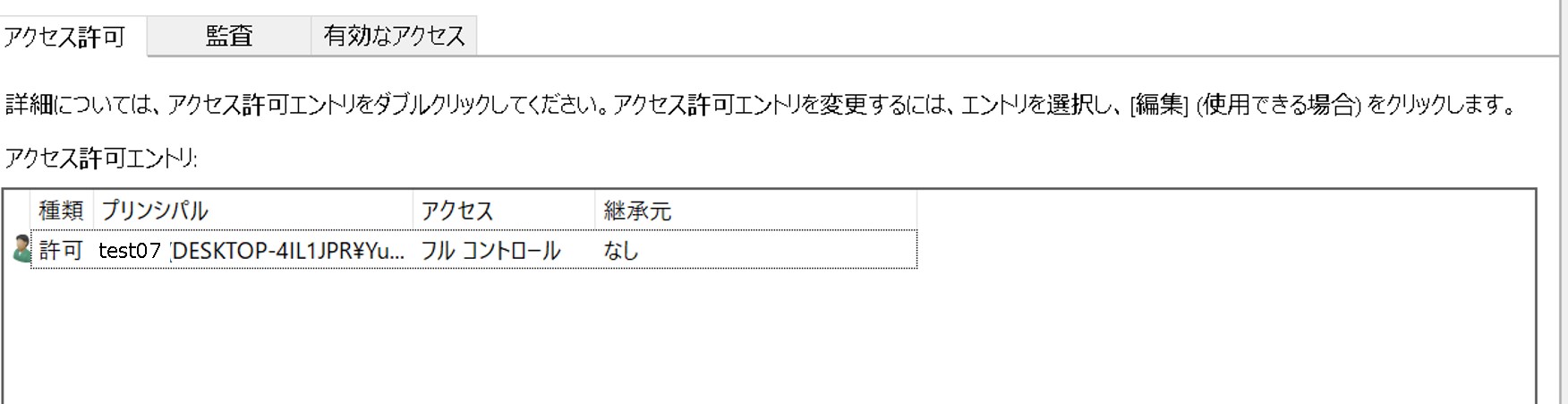
Run sftp.
Using a submission ID as the username
sftp authentication is based on the account, not on individual submissions.
For example, when uploading data to the DRA submission “test07-0001”, the following command is incorrect and will fail to log in:sftp -i id_rsa test07-0001@ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jpYou will see an error message like this:
Using username "test07-0001". Server refused our key.The correct command is:
sftp -i id_rsa test07@ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp -
Where to submit sequencing traces (chromatograms)?
- Sequencing data
- DTA
- DRA
Because the DDBJ Trace Archive will be integrated to SRA, we do not accept sequencing traces (chromatograms).
Please submit fastq files (bases and quality values) to DRA by choosing a Genetic Analyzer series instrument in the DRA Experiment Instrument Model. -
Which accession numbers should be cited in publication?
- Accession number
- BioProject
- BioSample
- DDBJ
- DRA
- GEA
- MetaboBank
Please cite accession numbers according to journal instructions.
It is recommended to cite accession numbers assigned to your data submissions, e.g. the DDBJ nucleotide sequence or DRA Run accession numbers.
Please cite a BioProject accession to reference all data from the project. It is necessary that metadata are described to enable users understand relationship between data in the publication and in the databases.DDBJ
Cite accession number(s) assigned to nucleotide sequence(s).
Prefix Letter ListDRA
Cite Run accession number(s) (prefix DRR) assigned to sequencing reads. Metadata
Please cite a BioProject accession to reference all data from the project. It is necessary that metadata are described to enable users understand relationship between data in the publication and in the databases.
Because data cannot be added to existing DRA submission, more than one DRA submission accessions will be created after data addition (Update). Therefore, citing DRA submission accessions (prefix DRA) is not recommended. Instead, we recommend to cite a BioProject accession.GEA
Cite Experiment accession “E-GEAD-n”.
GEA AccessionMetaboBank
Cite Study accession “MTBKSn”.
MetaboBank AccessionBioProject
If an individual BioProject needs to be referenced, state that “The data have been deposited with links to BioProject accession number PRJDBxxxxxx in the DDBJ BioProject database.” along with the accession numbers assigned to the data submissions.
BioSample
If an individual BioSample needs to be referenced, state that “BioSample metadata are available in the DDBJ BioSample database under accession number SAMDxxxxxxxx”.
-
How to request data release?
- Data release
- DDBJ
- BioProject
- BioSample
- DRA
- GEA
- MetaboBank
If you want to release your data, specify DDBJ/DRA/GEA/MetaboBank accession numbers to be released.
Database Example of Accession number How to request DDBJ AB12345678, ABCDEF010123456 Application Form for Data Update Requests form DRA DRR000001 Login to D-way and change the hold date GEA E-GEAD-1 GEA update request form MetaboBank MTBKS1 MeatboBank Update request form BioProject PRJDB1 BioProject/BioSample/DRA update request form BioSample SAMD00000001 BioProject/BioSample/DRA update request form How are linked BioProject/BioSample/experimental data released?
FAQ: How are linked BioProject/BioSample/sequence data released?
- When only BioProject accession is informed, only the BioProject record is released and related data are not released.
- When only BioSample accession is informed, only the BioSample record is released and related data are not released.
- DDBJ/DRA/GEA/MetaboBank data release triggers relase of referencing BioProject and BioSample.
-
How to submit sequence data related to the Barcode of Life (BoL)?
- Submission
- DDBJ
- DRA
For sequence data related to the Barcode of Life project, submit nucletide sequence(s) to DDBJ.
Trace chromatogram data from Sanger-type sequencers are not accepted. You may submit fastq files from Sanger-type sequencers to DRA. Submit fastq files and select a Sanger-type sequencer in the Experiment Instrument Model.
-
BioSample attribute file cannot be uploaded.
- attributes
- BioSample
Header must be enter with sample name
If you upload an Excel file instead of a tab-separated text (tsv) file, an error will occur.
If you are uploading a tsv file, please fill in the sample information from the second line, one sample per line.Please refer to the example of BioSample submission files.
For other messages and validation rules, please see the Validation rules page and upload the revised file.
-
Are fastq files of NCBI/ENA SRA not available?
- Downloading files
- DRA
We have stopped to generating fastq files from mirrored NCBI/ENA SRA data to save storage spaces since 11th December 2019. We have generated and will generate fastq files of DRA data.
- NCBI SRA: sra file only
- ENA SRA: sra and fastq files
- DDBJ SRA: Before 10th December 2019, sra and fastq files. After 11th December 2019, fastq of DRA only.
Archive sra files NCBI SRA fastq ENA SRA fastq DDBJ SRA fastq NCBI SRA O X X X ENA SRA O O O O DDBJ SRA O X (since 2019-12-10) X (since 2019-12-10) O For NCBI/ENA SRA data whose fastq files are not generated, you may obtain the fastq as follows.
Download from ENA
If ENA has generated fastq of the Run of your interest (for example, ERR3350433), you may download the fastq from ENA.
Download fastq from ENA Generating fastq from DRA mirrored sra file
Search the Run in DDBJ Search.
Example; ERR3350433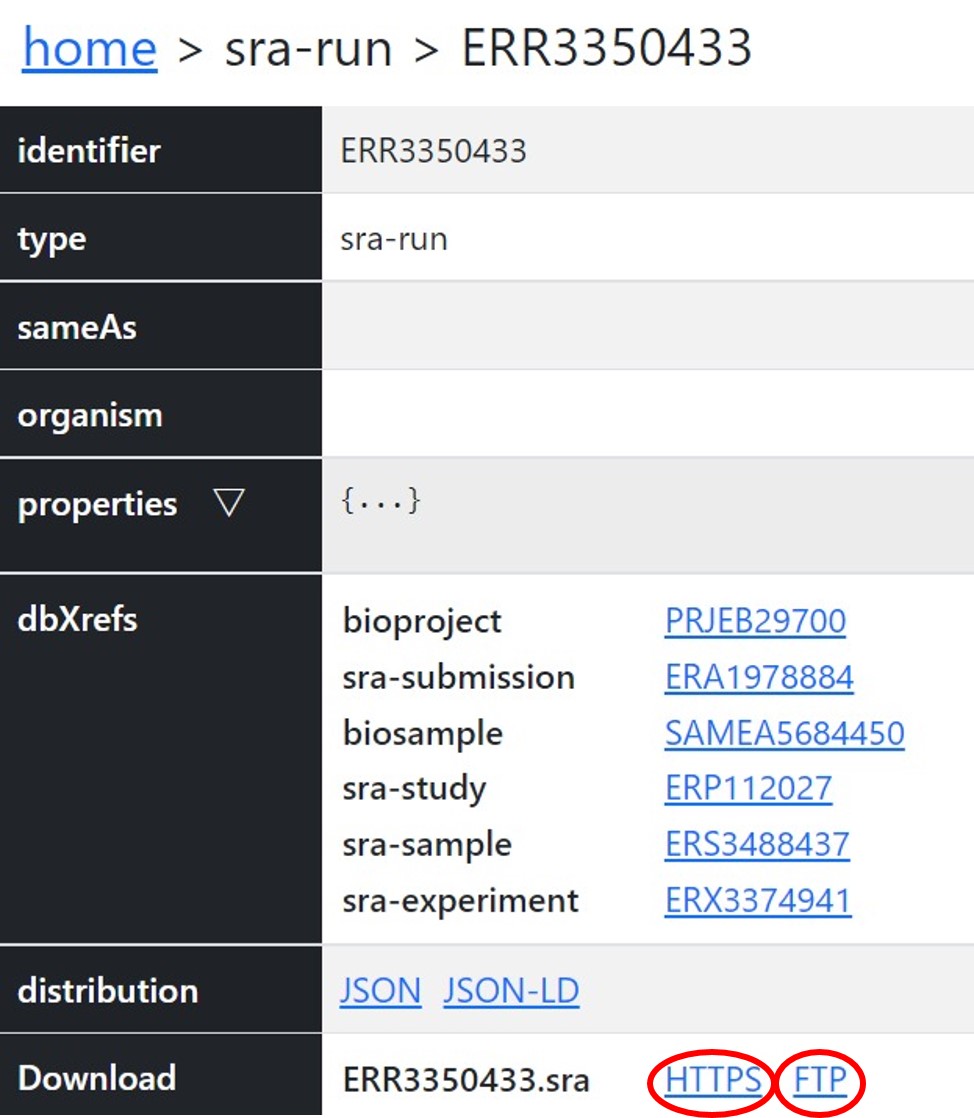
Download the sra file from DRA sra filepath;
- https://ddbj.nig.ac.jp/public/ddbj_database/dra/sralite/ByExp/litesra/ERX/ERX337/ERX3374941/ERR3350433/ERR3350433.sra
- ftp://ftp.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/ddbj_database/dra/sralite/ByExp/litesra/ERX/ERX337/ERX3374941/ERR3350433/ERR3350433.sra
Please see How to use prefetch and fasterq-dump to extract FASTQ-files from SRA-accessions regarding how to generate fastq from sra.
-
Unable to decrypt JGA data
- Decryption
- JGA
If you decrypt JGA data by using a PuTTY-format private key, an “Unable to load Private Key” error will be shown.
Convert a PuTTY-format private key into an OpenSSH-format key and use the OpenSSH-format private key.
Both OpenSSH and PuTTY format public keys can be registered in data use applications, you do not need to convert the registered public key format. -
How to find an appropriate BioSample attribute?
- attributes
- BioSample
Here is an example of how to find an appropriate attribute to describe “transplant recipient tissues”.
NCBI BioSample
If you have some idea, you may grasp the overview by seeing attribute name and their numbers in the NCBI BioSample Advanced Search Builder.
Select “Attribute Name” for the field name and input “transplant”, then names and their numbers are displayed. You may find most used name. If you want to see BioSample records using the name, select the name and search.
BioSample dump file
Download the BioSample XML file which contains all public records.
wget https://ddbj.nig.ac.jp/public/ddbj_database/biosample/biosample_set.xml.gzSearch attribute names and values by using grep.
grep "attribute_name=\"transplant" biosample_set.xml <Attribute attribute_name="transplant">intertidal</Attribute> <Attribute attribute_name="transplant">subtidal</Attribute> <Attribute attribute_name="transplant">subtidal</Attribute> <Attribute attribute_name="transplant">intertidal</Attribute> <Attribute attribute_name="transplanted with">non-targeting scramble shRNA control MLL-AF9 primary AML</Attribute> <Attribute attribute_name="transplanted with">non-targeting scramble shRNA control MLL-AF9 primary AML</Attribute> <Attribute attribute_name="transplanted with">Cdkn1b specific shRNA expressing MLL-AF9 primary AML</Attribute> ... -
I have an ancient DNA sample - how do I provide the spatiotemporal information for my sample?
- spatiotemporal
- BioSample
- DDBJ
For ancient DNA samples, the location and date to be reported depend on what information is important to interpret the sequencing data from the samples. If the original geographic location and original collection date are known and important to interpret the data, provide these information. If the sample was from a museum and the location of the museum and time of collection are important to interpret the data, enter these location and time. If relevant information does not exist, enter one of the missing values, e.g. “not collected”.
-
I am not able to report on my spatiotemporal metadata but my exemption reason is not on the list - what should I do?
- spatiotemporal
- BioSample
- DDBJ
If you feel unable to share these metadata but your exemption is not on the list, please contact us.
-
As part of my consortium, we set up an agreement that the data would be submitted to INSDC but that all metadata would not be shared until after 2 years. This agreement was organised prior to the standards change so we can’t comply. How do I report this?
- spatiotemporal
- BioSample
- DDBJ
This is considered a valid exemption as we recognise that some consortia will have agreements that pre-date the new standard and you can report this as a reason that the metadata are missing.
In this case, during initial sample registration you would report:
- geo_loc_name (or /country) = missing: data agreement-established pre-2023
- collection date = missing: data agreement-established pre-2023
Submissions can be updated at a later date to include the missing metadata.
-
What do I do if I can submit one of the mandatory fields but not the other?
- spatiotemporal
- BioSample
- DDBJ
We recognise there may be valid exemptions for this which are included for missing value reporting. For example, you may have collected a control sample from a collection instrument to sequence a negative control. In this case, the location of where you collected that control is not applicable to report as it was prepared in a lab but you could report the date in which you collected the control sample.
In this case, you would report:
- geo_loc_name (or /country) = missing: control sample
- collection date = 2020-05-25
-
Bioinformation and DDBJ Center had operated the gene expression database “CIBEX” (Center for Information Biology gene Expression database) until March 2012. All CIBEX date were migrated to GEA (Genomic Expression Archive).
Query BioProject with a CIBEX accession number (for example, CBX114) in DDBJ Search and follow a link to a corresponding GEA data.
A CIBEX accession number is retained in a GEA IDF metadata.
Comment[GEAAccession] E-GEAD-986 Comment[SecondaryAccession] CBX114 Comment[BioProject] PRJDB20087 -
If an error related to the checked directory occurs during the DRA validation, please contact the DRA team.
/mirror/submission/upload/test07/test07-0001/example.fastq -> /mirror/submission/checked/test07/test07-0001/example.fastq -
Cannot create a DDBJ Account due to duplication
- DDBJ Account
- DDBJ
- DRA
- GEA
- MetaboBank
- JGA
The username (account ID) for a DDBJ Account must be unique across both existing DDBJ Accounts and NIG Supercomputer Accounts. Please note that you cannot use a username (account ID) that is already used for the NIG Supercomputer.
-
How do I interpret the search results?
- Analysis
- BLAST
Search results are displayed in the following order. 1. Precedence table of sequences with high homology scores 1. Homologous sequences and their alignment 1. Parameters and statistics Note that the symbol “|” in the BLAST search results for nucleotide sequences indicates agreement between nucleotide sequences. For amino-acid sequences, matching amino acids will be displayed. The symbol “+” is used to indicate similarities between amino acids. For further details, refer the original papers on BLAST. [BLAST Reference](/blast-e.html#reference) -
Access to the ftp-private is blocked by the remote host key identification warning.
- Data transfer
- BioProject
- BioSample
- DDBJ
- DRA
- GEA
The BioProject/BioSample/DRA/GEA systems have been migrated to new supercomputer at 10th April 2025. Due to this migration, access to ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp may be blocked by the remote host key identification warning. ``` @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ @ WARNING: REMOTE HOST IDENTIFICATION HAS CHANGED! @ @@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@@ IT IS POSSIBLE THAT SOMEONE IS DOING SOMETHING NASTY! Someone could be eavesdropping on you right now (man-in-the-middle attack)! It is also possible that a host key has just been changed. The fingerprint for the ECDSA key sent by the remote host is SHA256:LAPCiua8RAlPIZwE4MKWX7YHMY//rtyjfnUYBj/cnfk. Please contact your system administrator. Add correct host key in /Users/test07/.ssh/known_hosts to get rid of this message. Offending ECDSA key in /Users/test07/.ssh/known_hosts:2 Host key for ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp has changed and you have requested strict checking. Host key verification failed. Connection closed ``` Delete a line where "ftp-private.ddbj.nig.ac.jp" or the IP address "133.39.224.111" are recorded from the known_hosts file under your home directory (for example, test07). /home/test07/.ssh/known_hosts You may know the line number to be deleted from the warning message (example below is 2). ``` Offending ECDSA key in /Users/test07/.ssh/known_hosts:2 ``` After deleting the line of the known_hosts file, access to the server. Because the access is regarded as a first time access, you are asked whether record the server key or not. Please select "yes" and access the server. -
Which taxonomy ID should be used for non-organism samples such as reference compound and buffer?
- attributes
- BioSample
Use the following taxonomy IDs for non-organism samples commonly used for metabolomics experiments. * [blank sample (taxid: 2582415)](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=2582415) * [unidentified (taxid: 32644)](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=32644) -
Which organism name should I use for non-living sample?
- Metadata
- BioSample
- MetaboBank
It is common to analyze non-living material samples in metabolomics experiments. For these samples, choose an appropriate name from [metagenomes](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Undef&id=408169&lvl=3&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock) of NCBI Taxonomy (please think excluding metagenome). Here are a few examples. * food sample: [food metagenome](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=870726&lvl=3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock) * soil sample: [soil metagenome](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Info&id=410658&lvl=3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock) For some non-living samples, please use names other than [metagenomes](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Undef&id=408169&lvl=3&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock). * blank measurement: "[blank sample](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?name=blank+sample)" * reference compound: "[unidentified](https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?id=32644)" -
How can I submit files when the files are too large or too many to upload from the MSS form?
- Mass Submission System
- DDBJ
If you are unable to upload submission files from the MSS form, please [upload the files by SFTP](/upload-e.html). -
How to describe samples labeled by isotopes?
- metadata
- MetaboBank
### Samples are metabolically labeled by isotopes When samples are labeled by metabolically uptaking stable isotopes (metabolic isotope labeling), describe isotope-labeled compounds in the “isotope_labeled_compound” attributes of BioSample records. Stable isotopes are described in the “isotope” attributes. These attributes are not included in [Omics package](/biosample/attribute-e.html?core=Standard&type=Omics), so please add these as user-defined ones. Example: * isotope_labeled_compound=[U-13C]-glucose * isotope=13C In the SDRF rows correspond to the samples, describe the compounds and isotopes in the Characteristics columns. |Characteristics[isotope_labeled_compound]|Characteristics[isotope]| |[U-13C]-glucose|13C| In this case, isotopes are described at sample-level, so the Labeled Extract Name and Label column values can be left empty. ### Extracted metabolites are chemically labeled by isotopes When samples are chemically labeled by isotopes (chemical isotope labeling), describe isotopes in the SDRF Label column and isotope-labeled compounds in the Comment[isotope_labeled_compound] column. |Labeled Extract Name|Label|Comment[isotope_labeled_compound]| |human urine sample 1 12C|12C|12C-dansyl chloride| |human urine pooled sample 13C|13C|13C-dansyl chloride| In this case, isotopes are described at the extract-level, so BioSample records may not contain attributes for isotopes. -
What is a SRA secondary accession?
- Accession number
- DRA
If a public SRA Run is replaced by a new Run, the previous accession will be a secondary accession of the new one to track replacement. For example, when DRR046787 was replaced by DRR049544, DRR049544 became primary and DRR046787 became secondary accession (below is the DRR049544 Run XML). ```DRR049544 DRR046787 454 GS Junior sequencing of SAMD00041397 -
My sample was collected in Shizuoka of Japan at 14:12:55 on the 5th May 2023. How do I format this for submission?
- spatiotemporal
- BioSample
- DDBJ
You should report the collection date in the format year-month-day followed by the time in ISO8601 standard format. Collection times must be in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). You should report the country and the region in an related field. For example: * geo_loc_name (or /country) = Japan:Shizuoka * collection date = 2023-05-05T05:12:55 -
I cultured and sequenced a bacterial strain distributed from a culture collection. How should I describe the location and time?
- spatiotemporal
- BioSample
- DDBJ
Enter the collection code and ID in [culture_collection](/biosample/attribute-e.html#culture_collection), and provide original location and date recorded in the collection. If original information is not known, use "missing: lab stock" of [missing values](/biosample/submission-e.html#missing-value-reporting). If the strain has been subcultured for a long term and its nature is changed, provide the date of sampling for sequencing. If the laboratory location is not appropriate for reporting, use "missing: lab stock" of [exemption terms](/biosample/submission-e.html#missing-value-reporting). In this case, describe the fact that "nature of the strain was changed by long-term subculture at the laboratory" in description. Example: [Arthrospira platensis NIES-39 strain](https://mcc.nies.go.jp/strainList.do?strainId=37&strainNumberEn=NIES-39) of the Microbial Culture Collection at the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES Collection). Collected at Lake Chad but the date is not recorded. * geo_loc_name (or /country) = Chad: Lake Chad * collection date = missing: lab stock -
I collected my sample for sequencing from a species outside of its natural environment (e.g. zoo, botanic garden) - how do I provide the spatiotemporal information for my sample?
- spatiotemporal
- BioSample
- DDBJ
For species originating elsewhere to where the sample was originally collected e.g. species in a museum, zoo, aquaculture, botanic garden or farm, describe the collection location which is useful to interpret the sequencing data obtained from the sample. If the museum, zoo, aquaculture, botanic garden or farm are important to interpret the data, enter these locations. If not, enter the location of origin. Treat the collection date in a similar manner. -
My sample was collected from the Pacific Ocean but the date was not recorded and I only know the year in which it was sampled was sometime in 2010 - how do I report this?
- spatiotemporal
- BioSample
- DDBJ
The minimum requirement is the name of the ocean/sea (or country) of the collection event and date to the nearest year. In this case, as you know the ocean and the year of collection, there is no reason that you can not share these metadata. You would report: * geo_loc_name (or /country) = Pacific Ocean * collection_date = 2010 -
If you want to change email addresses of Contact and Other Person
- Mass Submission System
- DDBJ
If you want to change email addresses of Contact and Other Person before the Accession number is issued, please send a request email to mass@ddbj.nig.ac.jp with the title included your NSUB number. After the Accession number has been issued, please contact us from "Update Contact Person Information" on our [site](https://www.ddbj.nig.ac.jp/ddbj/update-e.html).